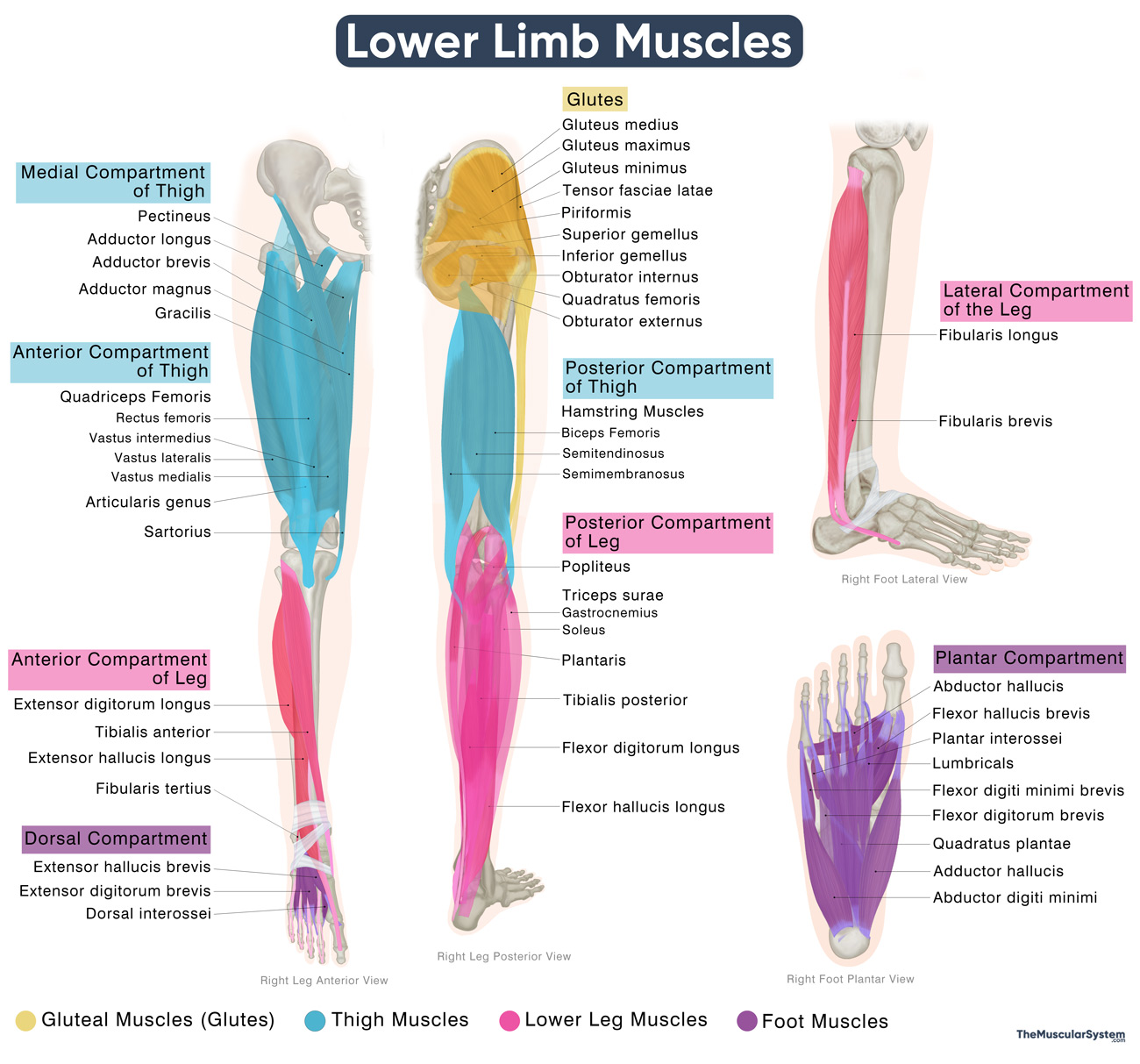
Lower Limb Muscles
The lower limb is the region of the body specialized for standing, walking, and running. It includes the hips, thigh, lower leg, and foot. These regions together contain powerful and coordinated muscles that flex (bend at a joint), extend, abduct (move away from the body’s midline), adduct (bring towards ), and produce other movements of the lower limb, allowing us to stand upright, walk, run, jump, and maintain balance.
Although the term “leg” is often used in everyday language to refer to the entire lower limb, in anatomical terms, it specifically refers to the region between the knee and the ankle. Throughout this article, the term “lower limb” will be used to describe the entire limb, while the muscles will be discussed according to their location.
List of the Muscles in the Lower Limb
The lower limb is divided into four main regions: the gluteal region, the thigh, the lower leg or leg, and the foot. The muscles within each of these regions are further classified based on their position, whether they lie at the front (anterior), back (posterior), or sides (medial or lateral) of the limb. They may also be grouped based on whether they make up the superficial or deep layer.
This classification helps describe both the muscles’ anatomical locations and their specific functions within the lower limb.
| Muscle Name | Location | Primary Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Gluteal Muscles (Glutes) | Muscles in the buttocks and outer hip region | – |
| Superficial | – | – |
| Tensor fasciae latae | Positioned on the outer hip and upper thigh | Stabilizes the hip and knee, abducts the thigh |
| Gluteus maximus | Forms the buttocks at the back of the hip | Extends and laterally rotates the hip |
| Gluteus medius | Situated on the outer side of the hip | Abducts and medially rotates the thigh |
| Gluteus minimus | Deep muscle on the outer hip surface | Abducts and medially rotates the thigh |
| Deep | – | – |
| Piriformis | Deep posterior hip | Laterally rotates and abducts the thigh |
| Obturator externus | Lies deep on the inner side of the hip | Laterally rotates the thigh at the hip |
| Superior gemellus | Deep muscle near the hip | Laterally rotates and abducts the thigh |
| Obturator internus | Located deep in the back of the hip | Laterally rotates the extended thigh |
| Inferior gemellus | Deep layer beneath the obturator internus | Laterally rotates and abducts the thigh |
| Quadratus femoris | Deep posterior hip | Laterally rotates the thigh |
| Thigh Muscles | Located between the hip and the knee | – |
| Anterior Compartment of the Thigh | Anterior thigh region | – |
| Articularis genus | Anterior thigh, near the knee | Elevates the synovial membrane during knee extension to protect the suprapatellar bursa |
| Sartorius | Runs obliquely across the anterior thigh | Flexes (bends), abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh |
| Quadriceps Femoris | – | – |
| — Rectus femoris | Middle of the front thigh region | Extends leg and flexes thigh |
| — Vastus lateralis | Outer front side of the thigh | Extends the leg at the knee |
| — Vastus intermedius | Deep anterior thigh, beneath the rectus femoris | Extends the leg at the knee |
| — Vastus medialis | Medial-anterior side of the thigh | Extends the leg and stabilizes the patella |
| Posterior Compartment of the Thigh | Posterior thigh region | – |
| Hamstring Muscles | – | – |
| — Biceps Femoris | Outer back side of the thigh | Flexes leg, extends thigh |
| — Semitendinosus | Inner back side of the thigh | Flexes leg and extends thigh |
| — Semimembranosus | Deep muscle on the inner back thigh | Flexes the leg, extends the thigh, and medially rotates the leg |
| Medial Compartment of the Thigh | The medial or inner thigh region | – |
| Gracilis | Innermost part of the thigh | Adducts the thigh, flexes, and medially rotates the leg |
| Pectineus | Upper inner thigh close to the groin | Adducts and flexes the thigh |
| Adductor brevis | Deep muscle within the inner thigh | Adducts the thigh and aids flexion |
| Adductor longus | Surface muscle on the inner thigh | Adducts and flexes the thigh |
| Adductor magnus | Large muscle on the inner back thigh | Adducts, flexes, and extends the thigh |
| Lower Leg Muscles | Muscles located between the knee and ankle | – |
| Anterior Compartment of the Leg | Front of the lower leg | – |
| Tibialis anterior | Front portion of the shin area | Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot |
| Extensor hallucis longus | Deep at the front of the leg, reaching the big toe in the foot | Extends the big toe, dorsiflexes the foot |
| Extensor digitorum longus | Front of the leg, reaching the four lateral toes in the foot | Extends toes, dorsiflexes the foot |
| Fibularis tertius | Front outer side of the lower leg, near the ankle | Dorsiflexes and everts the foot |
| Lateral Compartment of the Leg | Outer portion of the lower leg | – |
| Fibularis longus | The outer sides of the lower leg | Everts and plantarflexes the foot |
| Fibularis brevis | Deep muscle on the outer side of the lower leg | Everts and plantarflexes the foot |
| Posterior Compartment of the Leg | The calf region | – |
| Superficial | – | – |
| Triceps surae | The main muscle group at the back of the calf | – |
| — Gastrocnemius | A large surface muscle in the back of the calf | Plantarflexes the foot, flexes the knee |
| — Soleus | Under the gastrocnemius in the calf area | Plantarflexes the foot at the ankle |
| Plantaris | A small muscle in the upper back of the calf | Assists plantarflexion of the foot and flexion of the knee |
| Deep | – | – |
| Popliteus | Located behind the knee joint | Unlocks and flexes the knee |
| Muscles of the Tarsal Tunnel | – | – |
| — Flexor hallucis longus | From the back of the leg to the big toe in the foot | Flexes the big toe, plantarflexes the foot |
| — Flexor digitorum longus | From the back of the leg to the lateral toes in the foot | Flexes toes, plantarflexes foot |
| — Tibialis posterior | Deep leg muscle that supports the arch of the foot | Inverts and plantarflexes the foot |
| Foot Muscles | Muscles located in the ankle, tarsal, metatarsal, and toe areas | – |
| Dorsal Compartment of the Foot | Dorsum or the top surface of the foot | – |
| Extensor digitorum brevis | At the dorsum of the foot, near the four lateral toes | Extends 2nd-4th toes |
| Extensor hallucis brevis | At the dorsum of the foot, near the big toe | Extends the big toe |
| Plantar Compartment of the Foot | Sole or the bottom of the foot | – |
| First Layer | – | |
| Abductor hallucis | Inner side of the sole | Abducts and flexes the big toe |
| Flexor digitorum brevis | Middle area of the sole | Flexes the 2nd-5th toes |
| Abductor digiti minimi of the foot | Outer part of the sole | Abducts and flexes the little toe |
| Second Layer | – | – |
| Quadratus plantae | In the central sole area | Assists the flexor digitorum longus in toe flexion |
| Lumbricals of the foot | In the central sole area | Flexes metatarsophalangeal joints, extends toes |
| Third Layer | – | – |
| Flexor hallucis brevis | Inner sole under the big toe | Flexes the big toe |
| Adductor hallucis | Middle and outer sole areas | Adducts the big toe |
| Flexor digiti minimi brevis of the foot | Outer sole below the little toe | Flexes the little toe |
| Fourth Layer | – | – |
| Plantar interossei | Between the metatarsals on the foot sole | Adduct the 2nd-4th toes and flex their proximal phalanges |
| Dorsal interossei of the foot | Between the metatarsals on the top of the foot | Adduct the 3rd-5th toes and flex their proximal phalanges |
Innervation
The muscles of the lower limb receive innervation from the lumbosacral plexus, formed by the anterior rami of the first lumbar to fourth sacral spinal nerves (L1 to S4). Major branches of this plexus control distinct regions of the limb:
- Femoral nerve: Supplies the anterior thigh muscles responsible for hip flexion and knee extension.
- Obturator nerve: Innervates the medial thigh adductor muscles.
- Superior and inferior gluteal nerves: Supply the gluteal muscles
- Sciatic nerve: The largest nerve in the human body, it descends through the posterior thigh and divides into:
- Tibial nerve: Supplies the posterior leg and plantar foot muscles.
- Common fibular nerve: Innervates the anterior and lateral leg, and the dorsum of the foot.
Apart from the muscles, several important fasciae and ligaments provide structure and stability to the lower limb. The fascia lata, along with its thickened lateral portion, the iliotibial tract, supports the thigh and stabilizes the knee. The patellar ligament connects the kneecap to the tibia, assisting in knee extension. The Achilles tendon, the body’s strongest tendon, anchors the calf muscles to the heel bone and enables powerful plantarflexion during walking and running. Finally, the plantar fascia reinforces the arches of the foot and helps absorb shock during movement.
References
- Muscles of the Lower Limb: Radiopaedia.org
- Muscles of the Lower Limb: Medicine.UAMS.edu
- Lower Limb Anatomy: Kenhub.com
- Muscles of the Hips and Lower Limbs: Bio.Libretexts.org