Fibularis Tertius
Last updated:
10/09/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Fibularis Tertius
The fibularis tertius, also known as the peroneus tertius, is a small, thin unipennate muscle found at the front of the lower leg, just above the ankle, and extending down to the foot. It is the smallest of the four muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg, alongside the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and extensor digitorum longus.
The fibularis tertius is the only anterior muscle of the fibularis group, which otherwise consists of the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis situated in the posterior compartment.
Functionally, it assists in dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot, movements essential for walking, running, and maintaining balance.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
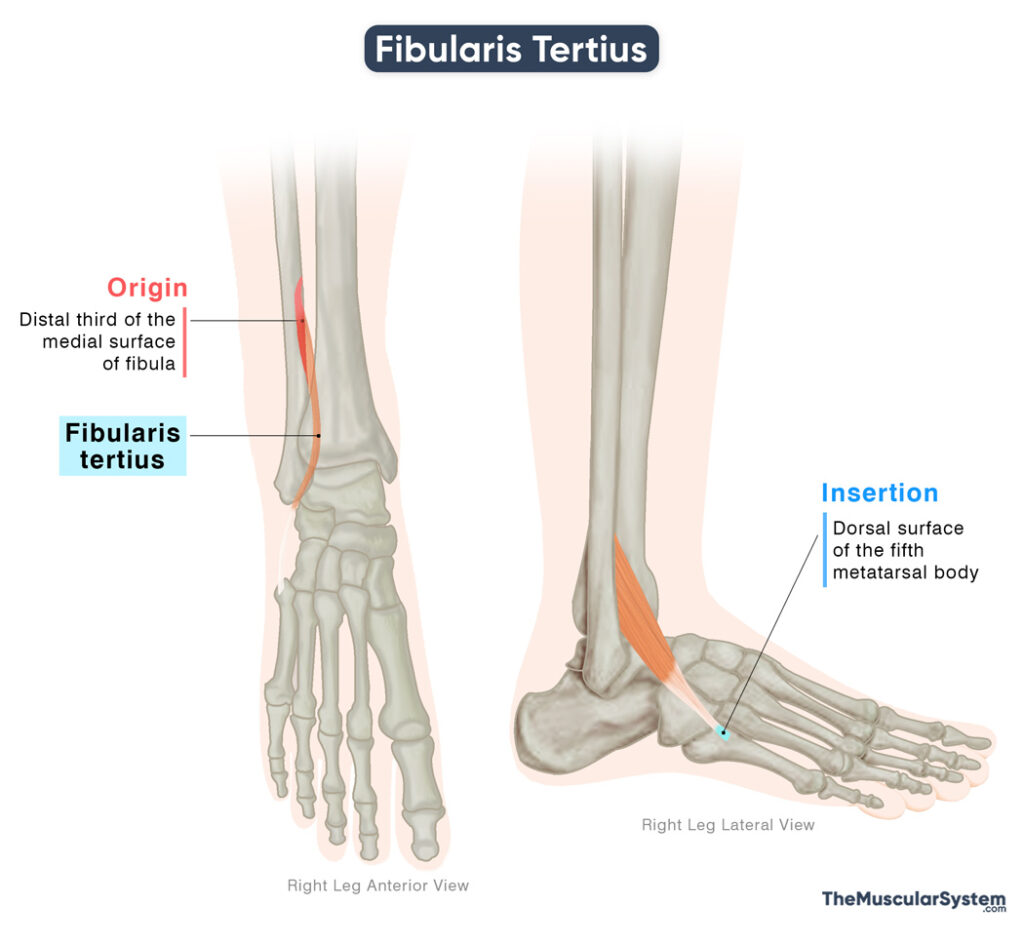
| Origin | The distal one-third of the medial surface of the fibula, and the adjacent interosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Dorsal surface of the body of the fifth metatarsal |
Origin
The muscle originates from three points:
- The distal one-third of the inner surface of the fibula, from the part just above the ankle joint. This is the primary point of origin.
- The front of the interosseous membrane that separates the fibula from the tibia.
- The front surface of the intermuscular septum that separates the anterior and posterior compartments of the lower leg (intermuscular septum of Otto)
Insertion
The fibers from all these origins descend laterally to form a single tendon. This tendon continues downwards, passing beneath the superior extensor retinaculum and then the inferior extensor retinaculum. It inserts into the upper-medial surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal, which is associated with the little toe.
Variation
Cadaveric studies show that the fibularis tertius is absent in as few as 5% and as many as 70% of people, depending on the population studied. In some Middle Eastern groups, the muscle was identified in only around 40% of individuals, while in North African populations, it was present in more than 65%. Despite this variability, its absence does not impair foot function or gait, as its role is compensated for by accessory peroneal muscles.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
In the lower leg region, the muscle is positioned in front of the fibula and the anterior compartment muscle, fibularis brevis. Medially, it is related to the distal third of the tibia, while laterally it runs alongside the extensor digitorum longus, with which it shares a common tendon sheath.
As it passes beneath the inferior extensor retinaculum, the tendon of fibularis tertius runs beside the tendons of extensor digitorum longus. Beyond the retinaculum, it continues to course alongside the four smaller tendons of extensor digitorum longus, which can make it appear as though it represents a fifth tendon of that muscle.
In the foot, the fibularis tertius lies superficial to the extensor digitorum brevis and anterior to the anterior lateral malleolar artery. As it courses along the dorsum of the foot, the tendon passes posterolateral to the talocalcaneonavicular joint and lateral to the tarsometatarsal joints.
Function
| Action | Dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot at the ankle |
Due to its position, the muscle cannot produce any large movements on its own. Instead, it assists the larger muscles in the area with various lower leg and foot movements. One interesting thing about the muscle is that it is rarely present in other primates. As a result, research has suggested that it contributes to the efficiency of bipedal, or two-legged, movement in humans.
Here are the main functions of the Fibularis Tertius:
- Weakly assisting the other muscles of the anterior compartment in dorsiflexing the foot at the ankle joint, meaning lifting the foot upward toward the shin.
- Acting in synergy with the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis to aid in eversion of the foot, meaning, turning the sole outward and away from the midline of the body.
Antagonists
The fibularis tertius has no distinct antagonist due to its small size and weak action. Functionally, however, the posterior compartment plantarflexors (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior) oppose its dorsiflexion, while the tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior counter its role in eversion through inversion.
Innervation
| Nerve | Deep fibular nerve (L5, S1) |
Like the rest of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the lower leg, this muscle is also innervated by the deep fibular artery from the fifth lumbar and first sacral nerve roots. It branches from the common fibular nerve, itself a branch of the sciatic nerve.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Anterior tibial artery |
The fibularis tertius is mainly supplied by the anterior tibial artery, a branch of the popliteal artery.
References
- Fibularis Tertius: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Fibularis Tertius Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Fibularis Tertius Muscle: Elsevier.com
- Fibularis Tertius Muscle: Radiopaedia.org
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts