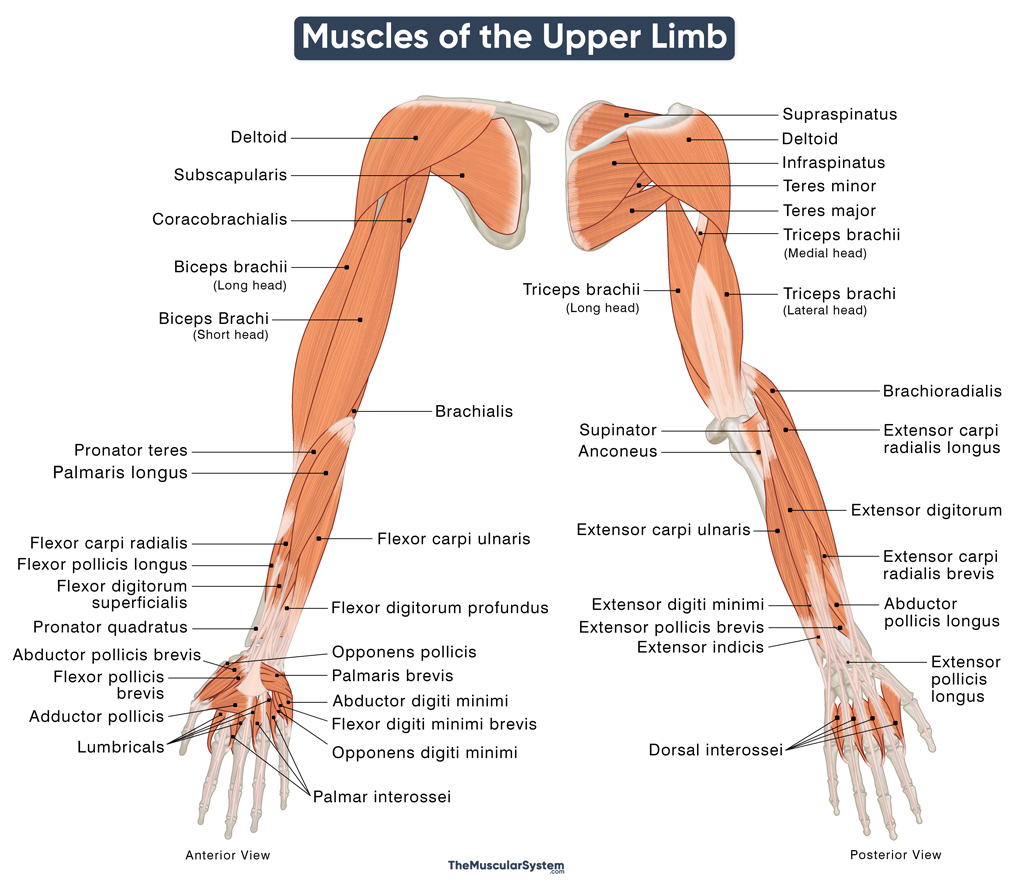
Upper Limb Muscles
The upper limb refers to the entire upper extremity in the human body, including shoulders, arms, hands, and fingers. So, all the muscles in this region are grouped as the upper limb or upper extremity muscles.
There are over 40 distinct muscles in the upper limb on each side, divided into the following groups:
These muscles are responsible for all movements of the upper extremity in the human body, from the smallest quiver of a finger to the biggest actions of the arm, like weightlifting.
Name, Location, and Anatomy of the Upper Limb Muscles
| Name | Origin | Insertion | Function | Innervation | Artery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Shoulder Muscles (6) |
|||||
| Deltoid | — Anterior: Lateral end of clavicle — Lateral: The upper surface and lateral margin of the acromion — Posterior: Lateral one-third of the scapular spine |
The deltoid tuberosity of the humerus | Flexion, rotation, abduction, and extension of the arm | Axillary nerve (C5-C6) | Thoracoacromial artery, subscapular artery, deep brachial artery, and the circumflex humeral arteries |
| Teres major | The inferior angle of the scapula | The bicipital groove of the humerus | Extension, adduction, and medial rotation of the arm at the shoulder | Lower subscapular nerve (C5-C7) | Subscapular artery and posterior circumflex humeral artery |
| — Rotator Cuff Muscles (4) | |||||
| — Supraspinatus | Supraspinous fossa of scapula | Superior aspect of the greater tubercle of humerus | Abduction of the arm (at 0-15°), stabilizing the shoulder joint | Suprascapular nerve (C5-C6) | Suprascapular artery |
| — Infraspinatus | Infraspinous fossa of scapula | The greater tubercle of humerus | Lateral rotation of the arm | Suprascapular nerve (C5-C6) | Suprascapular artery and circumflex scapular artery |
| — Teres minor | Upper 2/3rd of the lateral border of the scapula | Inferior aspect of the greater tubercle of humerus | Lateral rotation of the arm | Axillary nerve (C5-C6) | Subscapular, circumflex scapular, and posterior circumflex humeral arteries |
| — Subscapularis | Subscapular fossa of the scapula | Lesser tubercle of the humerus | Medial rotation of the arm | Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5-C6) | Suprascapular, axillary, and subscapular arteries |
Arm Muscles (Upper Arm Muscles) (5) |
|||||
Anterior Compartment (3) |
|||||
| Coracobrachialis | Coracoid process of the scapula | Medial aspect of the body of humerus | Flexion and adduction of the arm at the shoulder | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7) | Brachial artery |
| Biceps brachii | — Short head: Coracoid process (tip) of scapula — Long head: Supraglenoid tubercle of scapula |
Radial tuberosity and forearm’s deep fascia | Flexion and supination of the forearm | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C6) | Brachial artery |
| Brachialis | Anterior aspect of the distal humerus | Ulnar tuberosity and anterior aspect of ulna’s coronoid process | Flexion of the forearm | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C6) | Brachial and radial recurrent arteries |
Posterior Compartment (2) |
|||||
| Triceps brachii | — Long head: Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula — Lateral head: Posterior aspect of humerus, above the radial groove— Medial head: below the radial groove |
Olecranon of the ulna | Extension of the forearm at the elbow joint | Radial nerve (C6-C8) | Recurrent interosseous, and deep brachial arteries |
| Anconeus | Dorsal aspect of the lateral epicondyle of humerus | Olecranon and the posterior dorsal aspect of ulna | Extension of the forearm | Radial nerve (C6-C8) | Recurrent interosseous, and deep brachial arteries |
Forearm Muscles (19) |
|||||
Anterior Compartment (8) |
|||||
Superficial Anterior Forearm Muscles (5) |
|||||
| Pronator teres | — Humeral head: Medial supracondylar ridge of humerus — Ulnar head: Coronoid process of ulna |
Lateral aspect of radius | Pronation of the forearm | Median nerve (C6-C7) | Ulnar, radial, and brachial arteries |
| Flexor carpi radialis | The common flexor tendon | The base of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals | Flexion and abduction of the hand at the wrist | Median nerve (C6-C7) | Ulnar artery |
| Palmaris longus | The common flexor tendon | The flexor retinaculum, and palmar aponeurosis | Flexion of the wrist, and tightening the palmar aponeurosis | Median nerve (C7-C8) | Ulnar artery |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | — Humeral head: The common flexor tendon— Ulnar head: Olecranon of ulna | Pisiform, hook of hamate, 5th metacarpal base | Flexion and adduction of the hand at the wrist | Ulnar nerve (C7-T1) | Ulnar artery |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | — Humeroulnar head: The common flexor tendon, coronoid process of ulna, and ulnar collateral ligament — Radial head: Upper anterior border of the radius |
The base of 2nd to 5th middle phalanges | Flexion of the 2nd to 5th proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints | Median nerve (C7-T1) | Ulnar artery |
Deep Anterior Forearm Muscles (3) |
|||||
| Pronator quadratus | Anterior side of the distal ulna | Anterior side of the distal radius | Pronation of the forearm | Anterior interosseous nerve (C8-T1) | Anterior interosseous artery |
| Flexor digitorum profundus | Proximal 3/4 of the ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane | Base of the 2nd to 5th distal phalanges | Flexion of the 2nd-5th distal and proximal interphalangeal, and metacarpophalangeal joints | Anterior interosseous nerve (C8-T1) and ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Ulnar artery |
| Flexor pollicis longus | Anterior aspect of the radius and adjacent interosseous membrane | The palmar surface of the thumb’s distal phalangeal base | Flexion of the 1st interphalangeal joint (thumb) | Anterior interosseous nerve (C8-T1) | Anterior interosseous artery |
Posterior Compartment (11) |
|||||
Superficial Posterior Forearm Muscles (6) |
|||||
| Extensor digitorum | The common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle of humerus) | The extensor expansion of 2nd-5th digits | Extension of the 2nd-5th distal and proximal interphalangeal, and metacarpophalangeal joints | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior interosseous, anterior interosseous, and radial recurrent arteries |
| Extensor digiti minimi | The common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle of humerus) | The extensor expansion of the 5th digit | Extension of the 5th distal and proximal interphalangeal, and metacarpophalangeal joints | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Extensor carpi ulnaris | The common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle of humerus), and posterior ulna | Dorsal aspect of the 5th metacarpal’s base | Extension and adduction of the wrist | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Ulnar artery and posterior interosseous artery |
| — Mobile Wad Muscles (3) | |||||
| — Brachio-radialis | Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus | Styloid process on distal radius | Flexion and pronation of the forearm | Radial nerve (C5-C6) | Radial recurrent artery |
| — Extensor carpi radialis longus | Distal 1/3rd of the lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus | Dorsal aspect of the 2nd metacarpal’s base | Extension and abduction of the wrist | Radial nerve (C6-C7) | Radial artery |
| — Extensor carpi radialis brevis | The common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle of humerus) | Posterior aspect of the 3rd metacarpal’s base | Extension and abduction of the wrist | Deep radial nerve (C7-C8) | Radial artery |
Deep Posterior Forearm Muscles (5) |
|||||
| Supinator | Lateral epicondyle of humerus, supinator crest of ulna | Posterior aspect of the radius | Supination of the forearm | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Radial recurrent artery and posterior interosseous artery |
| Extensor indicis | Posterior aspect of distal ulna | Extensor hood of the 2nd digit (index finger) | Extension of the 2nd digit | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Abductor pollicis longus | Posterior aspects of the ulna and radius, along with the adjacent interosseous membrane | Base of the 1st metacarpal (thumb) | Extension and abduction of the 1st carpometacarpal joint | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Extensor pollicis brevis | Posterior aspect of the distal end of radius | Posterior aspect of the 1st proximal phalangeal base | Extension of the 1st carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Extensor pollicis longus | Posterior aspect of ulna, and the adjacent interosseus membrane | Posterior aspect of the 1st distal phalangeal base | Extension of the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the 1st digit (thumb) | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7-C8) | Posterior and anterior interosseous arteries |
Hand Muscles (11) |
|||||
Lateral Volar Muscles (4) |
|||||
| — Thenar Muscles (3) | |||||
| — Opponens pollicis | The tubercle of trapezium and attached flexor retinaculum | Radial aspect of the 1st metacarpal | Assisting in thumb opposition | Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8-T1) | Superficial palmar branch of radial artery |
| — Flexor pollicis brevis | — Superficial head: Tubercle of trapezium and adjascent flexor retinaculum— Deep head (if present): Trapezoid and capitate | Radial aspect of the 1st proximal phalangeal base | Flexion of the 1st metacarpophalangeal joint (thumb) | Recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8-T1) and Deep branch of ulnar nerve | Superficial palmar branch of radial artery |
| — Abductor pollicis brevis | The flexor retinaculum, and the scaphoid and trapezium bones | Lateral aspect of the 1st proximal phalangeal base | Abduction of the 1st carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints (thumb) | Recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8-T1) | Superficial palmar branch of radial artery |
| Adductor pollicis | — Oblique head: 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bases and the capitate bone— Transverse head: Palmar side on the shaft of 3rd metacarpal | 1st proximal phalangeal base | Adduction of the 1st carpometacarpal joint (thumb) | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Deep palmar arch |
Medial Volar Muscles (4) |
|||||
| — Hypothenar Muscles (3) | |||||
| — Abductor digiti minimi | Pisiform bone | Ulnar aspect of the 5th proximal phalangeal base | Abduction of the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint (little finger) | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Ulnar artery |
| — Flexor digiti minimi brevis | Hook of hamate and the adjacent flexor retinaculum | Ulnar aspect of the 5th proximal phalangeal base | Flexion of the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint (little finger) | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Deep palmar branch of ulnar artery |
| — Opponens digiti minimi | Hook of hamate and the adjacent flexor retinaculum | Ulnar aspect of the 5th proximal phalanx | Opposition and rotation of the 5th carpometacarpal joint (little finger) | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Deep palmar branch of ulnar artery |
| Palmaris brevis | Flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis | The skin covering the ulnar side of the palm | Strengthening the palmar grip | Superficial branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Superficial palmar arch |
Intermediate Volar Muscles (3) |
|||||
| Lumbricals | Flexor digitorum profundus muscle | Extensor expansion of 2nd to 5th digits | Flexion of the 2nd to 5th metacarpophalangeal joints, and extension of the same interphalangeal joints | Digital branches of median nerve (C8-T1), and deep branches of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Dorsal metacarpal, dorsal digital, and common palmar digital arteries |
| Dorsal interossei | — Medial head: Base of the 1st-4th metacarpals— Lateral head: Radial border of the 2nd-5th metacarpal | Base of the 1st-3rd proximal phalanges and the adjacent extensor expansion | Abduction and flexion of the 2nd-5th metacarpophalangeal joint and extension of the 2nd-5th interphalangeal joints | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Dorsal, and palmar metacarpal arteries |
| Palmar interossei | 1st, 2nd, 4th, and 5th metacarpals | Base of the 1st, 2nd, 4th, and 5th proximal phalanges the adjacent extensor expansion | Adduction and flexion of the 2nd-5th metacarpophalangeal joints, and extension of the 2nd-5th interphalangeal joints | Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1) | Palmar metacarpal arteries |
In addition to the above, the muscles in the chest or pectoral region play a vital role in connecting the upper limbs to the torso. These mainly include the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, and subclavius. Despite being included in the group of chest muscles, these are essential for the proper movement and functioning of many upper limb muscles.
Explore Related Concepts
FAQ
Q. Which are the biarticular (multi-joint) muscles in the upper extremity?
Ans. A muscle is considered biarticular when it crosses two joints or articulations rather than just one. In the upper limb, the biceps and triceps brachii muscles are the most notable examples of biarticular muscles as they span from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint.
References
- Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Muscles: NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
- Muscles of the Upper Limb: Medicine.UMICH.edu
- Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs: Lumenlearning.com
- Muscles of the Upper Limbs: Bio.libretexts.org
- Muscles of the Upper Limb: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Upper Limb Muscles and Movements: Kenhub.com
- Muscles of the Upper Limb: University.Pressbooks.pub
- Upper Limb: IMAIOS.com