Subclavius
Last updated:
05/05/2023Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Subclavius
The subclavius is a small, triangular muscle underneath the collarbone or clavicle. The primary function of this anterior thoracic wall muscle is stabilizing the clavicle during shoulder movements.
Anatomy
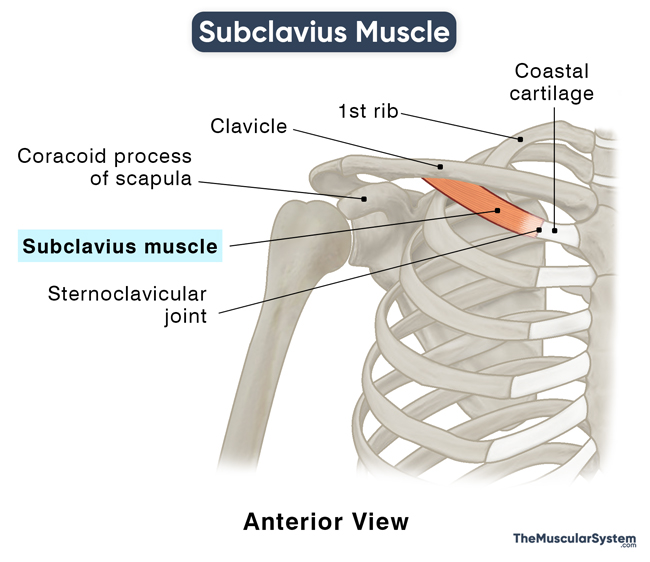
Location and Attachments
| Origin | Sternal end of 1st rib, at its costal cartilage junction |
| Insertion | The Middle-third of the clavicle’s Inferior surface, at the Subclavian groove |
Origin
The strong origin tendon of the subclavius emerges from the 1st rib, around the area where it articulates with the 1st costal cartilage. Then the tendon runs laterally and upward to expand into the muscle belly, finally inserting into the groove on the middle-third of the clavicle’s inferior surface.
Insertion
In certain anatomical variations, the insertion point may spread on to the coracoid process of the scapula along with, or instead of, the clavicle.
Relations to Other Muscular Structures
The subclavius lies deep to the pectoralis major muscle, along with the clavipectoral fascia. This fascia is the connective tissue between the clavicle and the pectoralis minor muscle and surrounds the subclavius.
The small muscle lies superficial to the brachial plexus, the subclavian artery and vein, and the suprascapular artery. These vessels separate the muscle belly from the 1st rib.
Functions
| Actions | Depressing and steadying the clavicle during shoulder movements |
- Its primary function is to keep the clavicle in place at the sternoclavicular joint (where the clavicle articulates with the sternum) during shoulder and arm movements.
- When the muscle contracts, it depresses the clavicle at its sternal end, which causes the first rib to elevate. Though this movement is rather insignificant under normal circumstances, it helps with forced breathing, like during an asthma attack.
- The presence of subclavius shields the superior trunk of the brachial plexus and the subclavian blood vessels from any damage if the clavicle is fractured.
Innervation
| Nerve | Subclavian nerve (C5 and C6) |
The subclavian nerve is a small branch of the brachial plexus (upper trunk).
Blood Supply
| Artery | Clavicular branch of the thoracoacromial artery |
The muscle has another minor source of blood supply from the suprascapular artery, a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, which in turn branches off from the subclavian artery.
References
- Subclavius: HealthLine.com
- The Subclavius Muscle: Structure and Function: Study.com
- Subclavius Muscle: KenHub.com
- Subclavius: Meddean.LUC.edu
- Subclavius Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Subclavius Muscle (Anatomy): GPnotebook.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts