Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Last updated:
23/05/2023Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is Abductor Pollicis Brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis (APB) is an intrinsic muscle of the hand in the thenar group located right underneath the skin. It can be palpated on the radial side at the base of the thumb on both the left and right hand when you abduct your thumb, which means moving it away from the rest of the fingers.
Like the other thenar muscles (opponens pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis), it primarily helps with thumb movements.
Anatomy
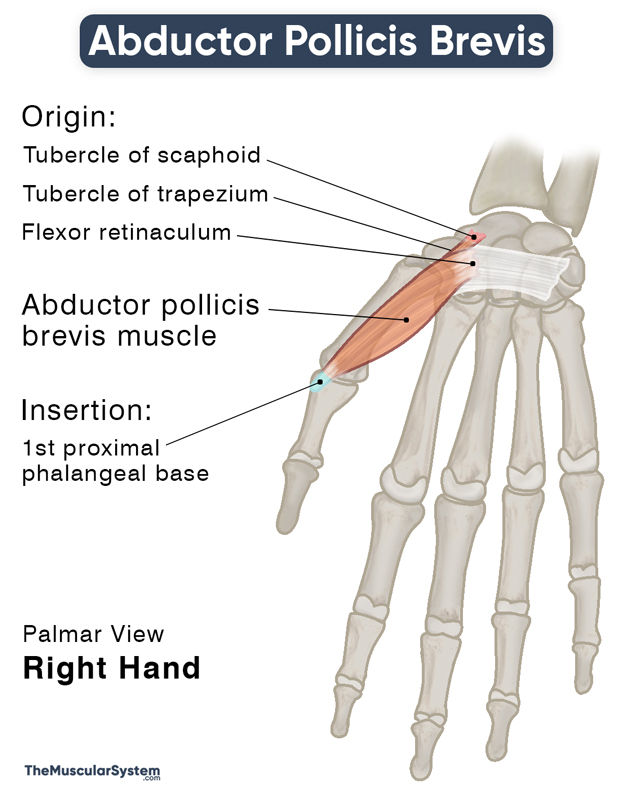
Location and Attachments
| Origin | The flexor retinaculum and the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium |
| Insertion | Lateral surface of the 1st proximal phalangeal base |
Origin
The thin, flat fusiform muscle has multiple points of origin, with the primary part arising from the flexor retinaculum. There are 2 smaller slips arising from the tubercles of the two carpal bones, scaphoid and trapezium. Often, another small slip rises from the abductor pollicis longus muscle’s tendon, joining the APB’s belly from the lateral side.
Insertion
The muscle belly then runs distally and laterally toward the thumb’s phalanges. It narrows down into a thin tendon to insert into the lateral or radial surface of the base of the 1st proximal phalanx. A few lateral slips also attach to the inserting tendons of the extensor pollicis longus.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
As mentioned above, abductor pollicis brevis is the most superficial muscle in the thenar eminence, lying superior to the other two thenar muscles, opponens pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis. The gap formed by these three muscles allows the median nerve’s thenar branch to pass.
Function
| Action | Abduction of the thumb at the 1st carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints |
As its name suggests, it abducts the thumb at its carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints. It also acts on the metacarpophalangeal joint when the thumb is flexed across the palm to touch the other fingertips (opposition). Its action is synergistic to that of the abductor pollicis longus.
The APB, being a thenar muscle, helps with all the tasks that need the use of your fingers and thumb for precision, like picking up a small round object, holding a pen, or sewing with a needle.
The primary antagonist of this muscle is the adductor pollicis.
Innervation
| Nerve | Recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8 and T1) |
Blood Supply
| Artery | Superficial palmar branch of radial artery |
The superficial palmar branch of the radial artery courses over the superficial surface of the abductor pollicis brevis and acts as the muscle’s primary blood supply.
References
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis:WheelessOnline.com
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle: KenHub.com
- The Attachments And Function Of The Abductor Pollicis Brevis: NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: IMAIOS.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Infrahyoid Muscles
- -
Omohyoid
- -
Sternohyoid
- All Posts