Opponens Pollicis
Last updated:
11/05/2023Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is Opponens Pollicis
The opponens pollicis is a thenar muscle that forms the thenar eminence, the fleshy mound on the palm at the base of the thumb. It is the largest of the 3 thenar muscles, the other two being the abductor pollicis brevis and flexor pollicis brevis.
This short intrinsic muscle, along with the rest of the thenar muscles, helps with thumb opposition.
Anatomy
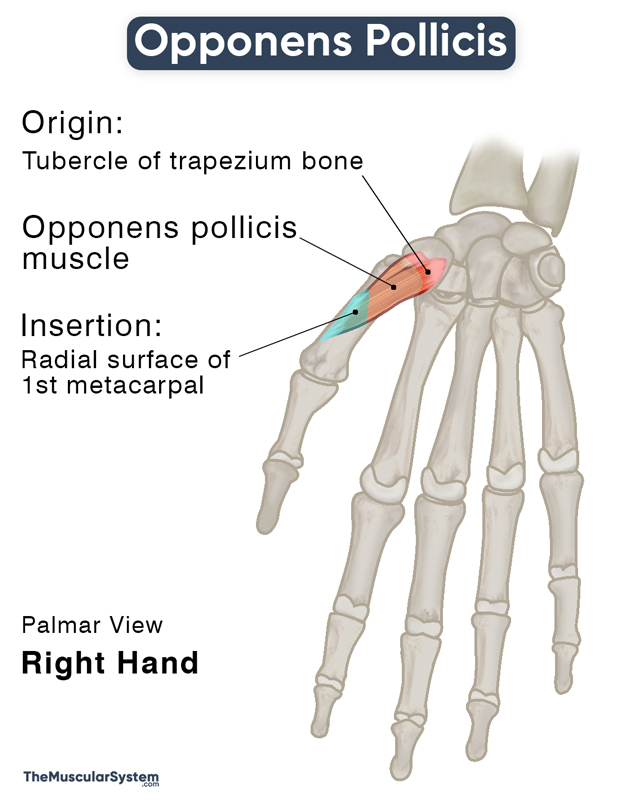
Location and Attachments
| Origin | Tubercle of the trapezium and the attached flexor retinaculum |
| Insertion | Radial surface of the 1st metacarpal |
Origin
As already mentioned, it is a short muscle that courses distally and radially from its point of origin at the tubercle of the trapezium, the carpal bone at the base of the thumb.
Insertion
The muscle belly then narrows into a tendon to insert into the entire length of the radial or lateral side of the 1st metacarpal’s shaft.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
Being a thenar muscle, it is located on the radial side of the hand, deep to the abductor pollicis brevis. The flexor pollicis brevis lies medially, with its superficial head often blending with the opponens pollicis.
Function
| Action | Assisting in thumb opposition at the 1st carpometacarpal joint |
Opposition of the thumb refers to the flexion, adduction, and rotational movements that let the thumb touch the other fingers and move away from them.
As its name suggests, contraction of the opponens pollicis flexes the first metacarpal and brings the thumb across the palm to touch the other fingers. It also helps with the medial rotation of the thumb.
The movements produced by thumb opposition help with precise hand movements and dexterity. The actions of the opponens pollicis plays a vital role in the pincer grasp that allows you to grasp or pinch objects using the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger, like holding a pen or picking up a round object.
Innervation
| Nerve | Recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8, T1) |
The median nerve’s recurrent or thenar branch provides the primary innervation to this muscle. In some people, the deep terminal branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the muscle.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Superficial palmar branch of radial artery |
The superficial palmar branch that rises from the radial artery is the main source of blood supply to the opponens pollicis. Additional blood supply may come from the deep palmar arch, formed by the terminal part of the radial artery, as well as from the princeps pollicis and radialis indicis arteries.
References
- Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Opponens Pollicis Muscle: NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
- Opponens Pollicis (OP): NerveSurgery.WUSTLl.edu
- Opponens Pollicis Muscle: KenHub.com
- Opponens Pollicis: RAD.Washington.edu
- Opponens Pollicis: TeachMeAnatomy
- Opponens Pollicis Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts