Extensor Pollicis Brevis
Last updated:
05/06/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is Extensor Pollicis Brevis
The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a slender, flat muscle in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm. Relatively short for a forearm muscle, it is one of the three muscles forming the boundaries of the anatomical snuff box. The abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis longus are the two other muscles contributing to this anatomical space in the hand.
Anatomy
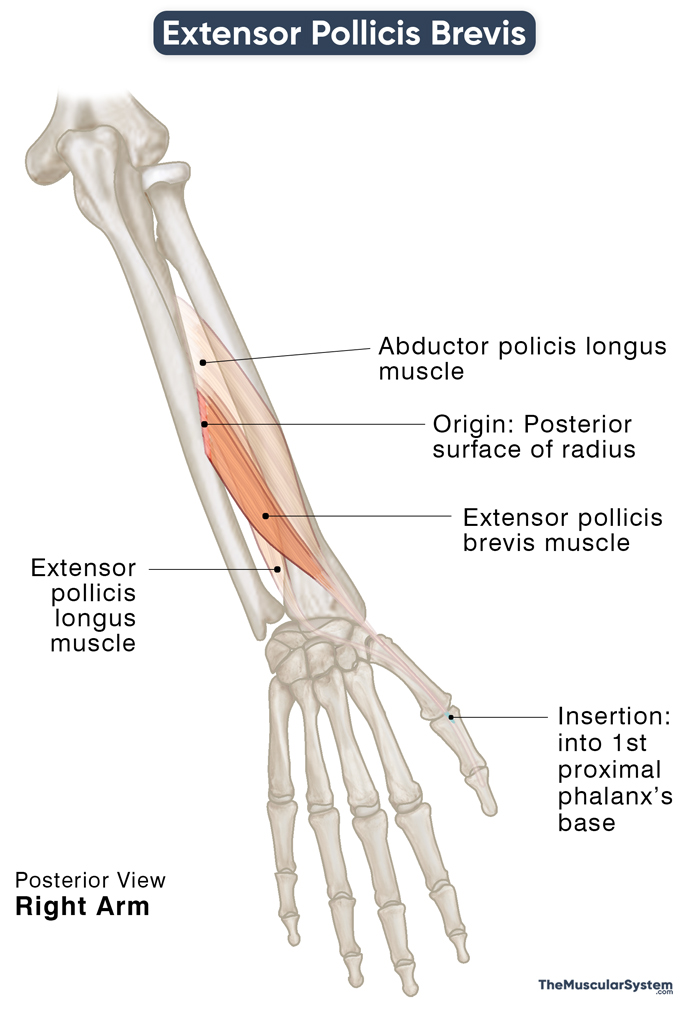
Location and Attachments
| Origin | The posterior surface of the radius’s distal one-third |
| Insertion | The posterior surface of the 1st proximal phalangeal base |
Origin
The extensor pollicis brevis originates from the back of the radial shaft at its distal side. Some muscle fibers also originate from the interosseous membrane that runs from the radius to the ulna. The point of attachment on the radius lies just inferior to the point where the abductor pollicis longus, the other longer, deep posterior forearm muscle, originates.
Insertion
The muscle belly runs distally, narrowing into a tendon just before the wrist. The tendon runs between the superficial posterior muscle extensor carpi radialis longus and the abductor pollicis longus to pass deep to the extensor retinaculum. The muscle courses further distally, alongside the abductor pollicis longus, sharing the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist. It then enters the hand on its dorsal surface and inserts at the base of the 1st proximal phalanx (of the thumb).
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The extensor pollicis brevis has the extensor digitorum lying superficial to it, while the abductor pollicis longus lies laterally. The extensor pollicis longus runs anterolateral to the EPB.
On the distal side, just before it reaches the wrist, the EPB tendon crosses the extensor carpi radialis brevis and longus tendons obliquely before passing underneath the extensor retinaculum.
Near the wrist, the tendon forms the radial border of the anatomical snuff box along with the abductor pollicis longus tendon. The anatomical snuff box is a triangular depression on the radial side of the hand at the base of the thumb. It is where the radial pulse is taken as the radial artery passes through this space.
Function
| Action | Extension of the thumb at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints |
Along with the extensor pollicis longus, this muscle primarily acts on the 1st metacarpophalangeal joint to extend or straighten the thumb. The muscle also acts on the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb to extend it.
Both these actions are essential for all movements and functions of the thumb. The muscle plays a vital role in opening a grip to let go of something held in your hand.
Another minor function of the extensor pollicis brevis is assisting the extensors and abductors of the wrist in their action.
Innervation
| Nerve | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7 and C8) |
The posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8), continuing from the radial nerve’s deep branch, innervates the extensor pollicis brevis.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Posterior interosseous artery |
The posterior interosseous artery supplies the muscle’s primary vasculature, while the perforating branches of the anterior interosseous artery provide an additional supply. Both are branches of the ulnar artery.
References
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis: Anatomy.app
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle: KenHub.com
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis: IMAIOS.com
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis: Rad.Washington.edu
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts






One thought on “Extensor Pollicis Brevis”-
Pingback: Posterior Forearm Muscles (Extensors): Names, Anatomy, Diagram