Posterior Forearm Muscles (Forearm Extensors)
Last updated:
04/06/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
The part of the hand between the elbow and wrist is called the forearm or antebrachium. Now, there are several muscles that shape the forearm and help it function. These muscles are divided into the anterior and posterior compartments.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains the muscles that lie at the posterior aspect of the forearm. There are 11 muscles in the posterior compartment, also called the extensor compartment.
Forearm Extensors with Names, Anatomy, & Functions
These muscles are together referred to as the extensors and are further divided into two groups based on their location: superficial and deep.
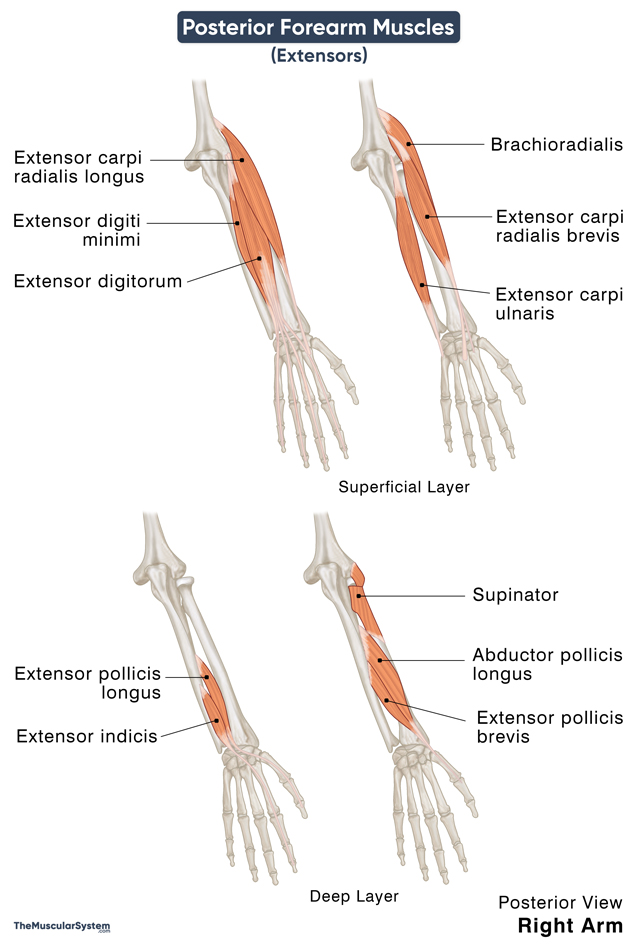
| Muscle Name | Location Layer | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Extensor digitorum | Superficial | The lateral epicondyle of the humerus via the common extensor tendon | The extensor expansion of 2nd to 5th digits | Extending the index finger to little finger | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 2. Extensor digiti minimi | Superficial | Via common extensor tendon | The extensor expansion of the 5th digit | Extending the little finger | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 3. Extensor carpi ulnaris | Superficial | Via common extensor tendon; Ulna’s posterior border | Base of the 5th metacrpal | Extending and adducting the wrist | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 4. Brachioradialis | Superficial | Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus | Styloid process of the radius | Flexing the elbow*, pronating the forearm | Radial nerve (C5, C6) |
| 5. Extensor carpi radialis longus | Superficial | Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus | Base of the 2nd metacarpal | Extending and abducting the wrist | Radial nerve (C6, C7) |
| 6. Extensor carpi radialis brevis | Superficial | Via common extensor tendon | Base of the 3rd metacarpal | Extending and abducting the wrist | Radial nerve (C7, C8) |
| 7. Supinator | Deep | Lateral epicondyle of humerus; supinator crest of ulna | Posterior side of the radius | Supinating the forearm | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 8. Extensor indicis | Deep | Posterior surface of distal ulna | The extensor expansion of the 2nd digit | Extending the index finger | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 9. Abductor pollicis longus | Deep | Posterior surface of radius and ulna; interosseus membrane | Base of the 1st metacarpal | Extending and abducting the thumb | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 10. Extensor pollicis brevis | Deep | Posterior surface of distal radius | Base of 1st distal phalanx | Extending the thumb | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| 11. Extensor pollicis longus | Deep | Posterior surface of ulna; interosseus membrane | Base of 1st distal phalanx | Extending the thumb | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
*The brachioradialis muscle works as a flexor and pronator despite being part of the extensor group of muscles in the forearm. It is the only muscle in this compartment to take part in flexion.
The 3 superficial muscles brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis constitute the mobile wad of Henry, a lateral compartment within the posterior compartment.
The abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and extensor pollicis longus tendons on the distal side form the medial and lateral boundaries of the anatomical snuff box, the triangular depression at the base of the thumb.
References
- Deep Posterior Forearm Muscles: KenHub.com
- Superficial Posterior Forearm Muscles: KenHub.com
- Muscles in the Posterior Compartment of the Forearm: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Posterior Compartment of Forearm: IMAIOS.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts





