Extensor Digiti Minimi
Last updated:
05/05/2023Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is Extensor Digiti Minimi
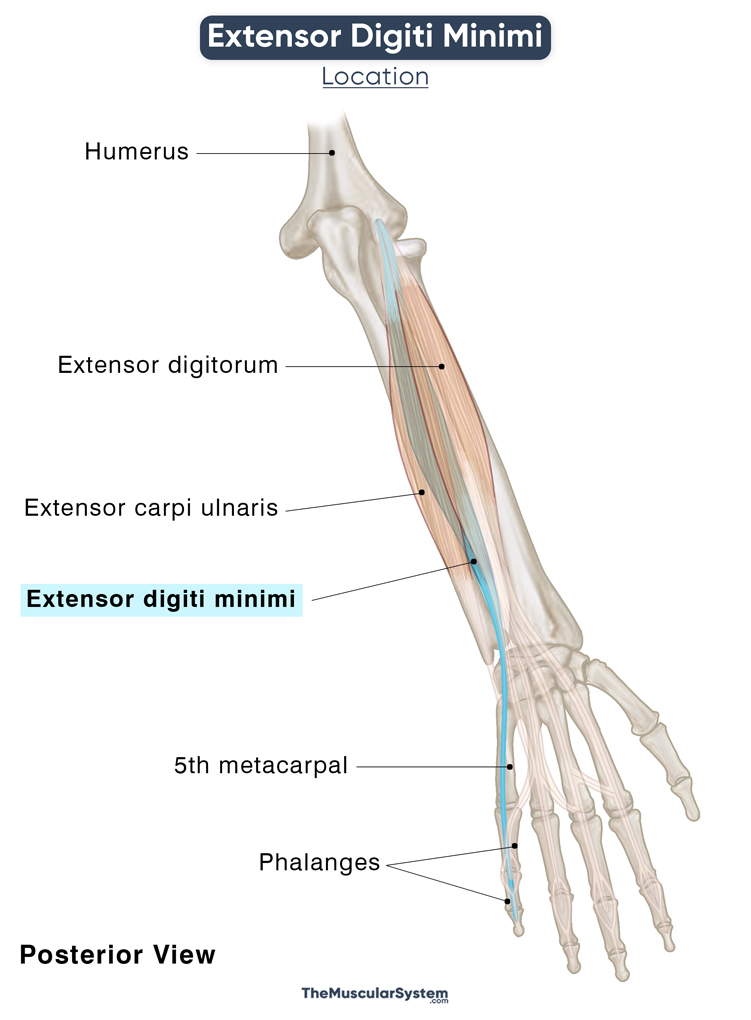
The extensor digiti minimi (EDM) is a superficial muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearms. This long narrow muscle is one of the 6 superficial extensors of the forearm, the others being the extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris, brachioradialis, and the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis. It is an extrinsic muscle of the hand, with its origin in the humerus.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
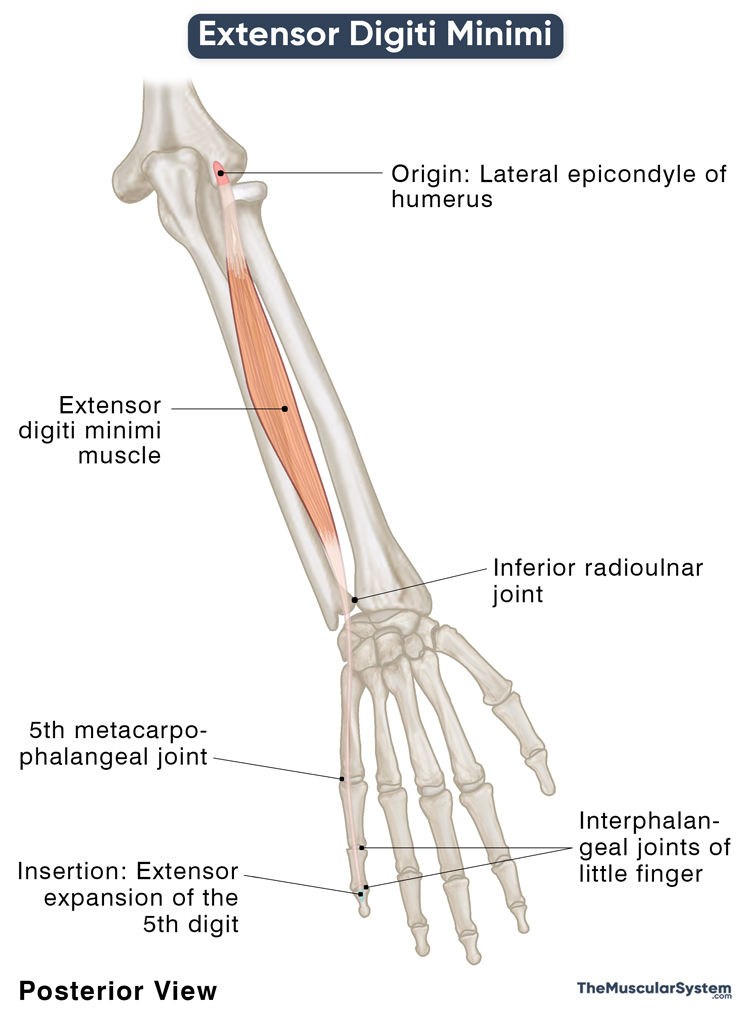
| Origin | Lateral epicondyle of the humerus (the common extensor tendon) |
| Insertion | Extensor expansion of the 5th digit |
Origin
The muscle shares its origin with the extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris, and extensor carpi radialis brevis, all arising via the common extensor tendon from the lateral epicondyle.
Some of the EDM’s originating fibers may be fused with the extensor digitorum. As the muscle travels downward, its fibers gradually separate from the extensor digitorum. The extensor digiti minimi becomes recognizable as an independent muscle halfway down the forearm.
Insertion
The muscle belly then narrows into a long thin tendon that continues distally down the forearm, passing deep to the fibrous band of the extensor retinaculum. As it enters the dorsal surface of the hand, it deviates slightly towards the 5th digit (little finger) and divides into two small slips that insert into the digit’s extensor expansion or hood. It is the broad aponeurotic sheet that covers the dorsal surface of the little finger, the area between the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The extensor digitorum muscle lies lateral to the extensor digiti minimi once the fibers of the two muscles separate and run their own course. The extensor carpi ulnaris is located medial to the EDM.
On the distal side, its tendons lie deep to the ulnar artery’s dorsal carpal branch and the ulnar nerve’s dorsal branch. The nerve and blood vessels cross the tendons around the wrist, where the muscle passes underneath the extensor retinaculum, the only barrier keeping them separate.
The extensor digiti minimi tendon forms the 5th dorsal extensor compartment as it crosses the inferior radioulnar joint from behind.
Functions
| Action | Extension of the little finger at all its joints |
- With the insertion in its extensor expansion, the primary function of extensor digiti minimi is to extend the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
- It works with the extensor carpi ulnaris to help the little finger extend at the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints too.
- Being the exclusive extensor muscle attached to the little finger, it helps the finger extend independently, like when you do a pinkie swear.
- The muscle plays a minor role in wrist extension as well.
The primary antagonist of extensor digiti minimi is the hand muscle, flexor digiti minimi brevis.
Innervation
| Nerve | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7 and C8) |
The posterior interosseous nerve that innervates this muscle is a branch of the radial nerve (deep branch), which branches from the brachial plexus’s posterior cord.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Posterior interosseous artery |
The posterior interosseous artery, a branch of the ulnar artery via the common interosseous artery, is the primary source of blood supply to this muscle.
Additionally, is it supplied by the radial recurrent artery — a branch of the radial artery.
References
- Extensor Digiti Minimi: IMAIOS.com
- Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle: KenHub.com
- Extensor Digiti Minimi: Rad.Washington.edu
- Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle: Bionity.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Infrahyoid Muscles
- -
Omohyoid
- -
Sternohyoid
- All Posts