Adductor Longus
Last updated:
21/08/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Adductor Longus
The adductor longus is a large, triangular muscle in the inner thigh region. It belongs to the group of hip adductors in the medial compartment of the thigh, along with the gracilis, pectineus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus. It plays a major role in various movements of the lower limb at the hip joint, like moving the thighs closer, folding, and rotating them.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
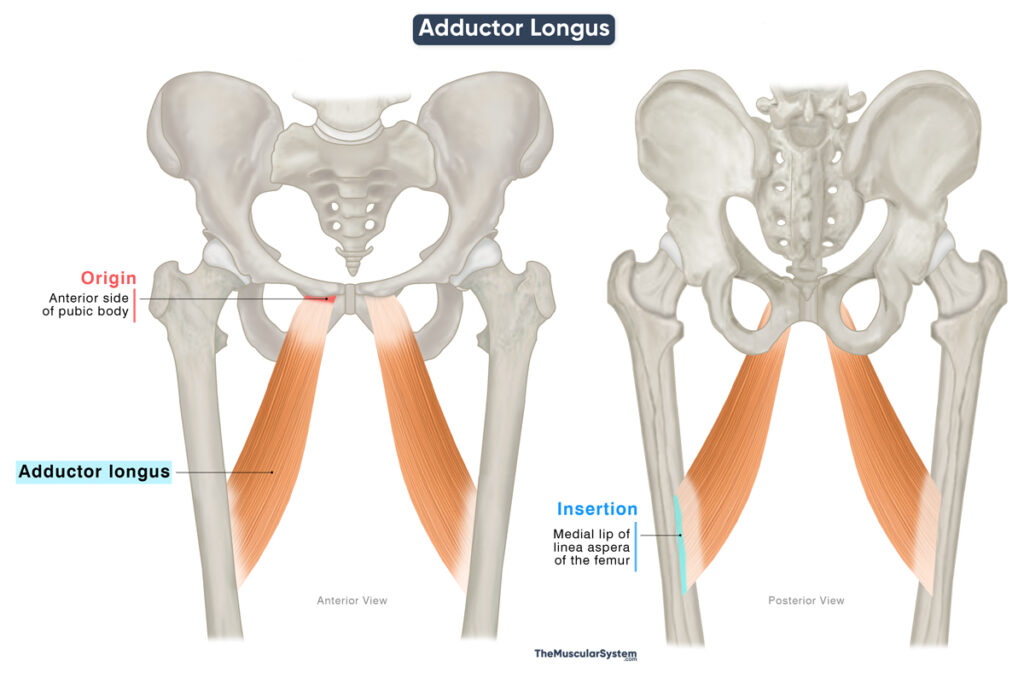
| Origin | Anterior surface of the pubic body |
| Insertion | Medial lip of the middle one-third of the linea aspera of the femur |
Origin
The muscle originates as a small, narrow tendon from the anterior surface of the body of the pubis bone. The point of origin lies just below the pubic crest and on the lateral side of the pubic symphysis.
Insertion
From this origin, the muscle fibers spread in a fan-like manner, forming a thick, broad muscle belly that extends laterally, backward, and downward toward the femur. The fibers then converge into a broad aponeurosis, which inserts onto the medial lip of the linea aspera along its middle third.
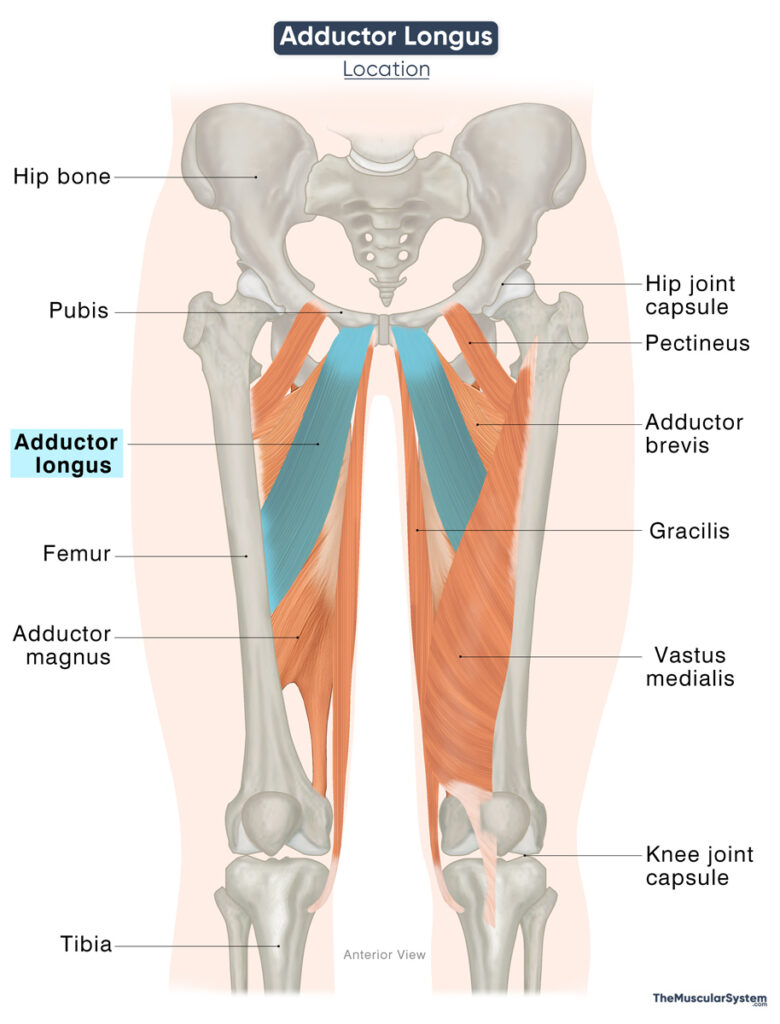
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The muscle is located in the medial compartment of the thigh, lying in front of the adductor brevis and adductor magnus. Within this compartment, the pectineus muscle lies lateral to it, and the gracilis lies medially. The upper-inner portion of the fascia lata covers the muscle superficially. At the distal end, its femoral attachment lies adjacent to the vastus medialis muscle’s origin.
The adductor longus forms the medial border of the femoral triangle, a triangular depression in the upper inner thigh. Along with the adductor magnus, it contributes to the posterior wall of the adductor canal, an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle thigh through which major neurovascular structures pass to the lower limb.
Posterior to the adductor longus run the anterior branch of the obturator nerve and the profunda femoris (deep femoral) artery and vein. In contrast, the femoral artery and vein cross anterior to the distal part of the muscle, near its insertion.
Function
| Action | Adducting, flexing, and rotating the thigh at the hip joint |
The adductor longus is a vital muscle in everyday movements such as walking, running, and climbing. Its functions include:
- Contracting in synergy with the other hip adductors to adduct the thigh at the hip joint, which means bringing the thighs closer together.
- Stabilizing the hip joint when walking or standing.
- Assisting the hip flexors, including the iliopsoas and rectus femoris, to flex the hip joint, which means folding the thigh at the hips.
- Contributing (weakly) to both lateral and medial rotation of the thigh, depending on the position of the thigh.
Antagonists
The hip abductors, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae, act as antagonists to the adductor longus, moving the thigh away from the midline.
Innervation
| Nerve | Obturator nerve (L2-L4) |
The muscle is innervated by the anterior branch of the obturator nerve, a branch of the lumbar plexus derived from the ventral rami of the L2–L4 spinal nerves.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Profunda femoris, and obturator arteries |
The primary blood supply comes from the profunda femoris or deep femoral artery, which branches from the femoral artery, and the obturator artery, which branches from the internal iliac artery. The medial circumflex femoral artery, a branch of the profunda femoris, may also provide additional vascular supply to the proximal portion of the muscle.
References
- Adductor Longus: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Adductor Longus Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Adductor Longus Muscle: Radiopaedia.org
- Adductor Longus: Elsevier.com
- Adductor Longus: IMAIOS.com
- Adductor Longus: Rad.UW.edu
- Adductor Muscles: Magnus, Longus & Brevis | Adductor Function & Types: Study.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts