Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Last updated:
08/10/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Extensor Digitorum Brevis
The extensor digitorum brevis, or EDB, is a small intrinsic muscle on the dorsal surface of the foot. It belongs to the dorsal compartment of the foot with the extensor hallucis brevis. The EDB helps extend the second to fourth toes during movements such as walking and balance.
The muscle can be easily seen and felt as a fleshy lump, just in front of the bony bump on the outer side of the ankle (lateral malleolus), when you bend your foot upward towards the shin in dorsiflexion.
Anatomy
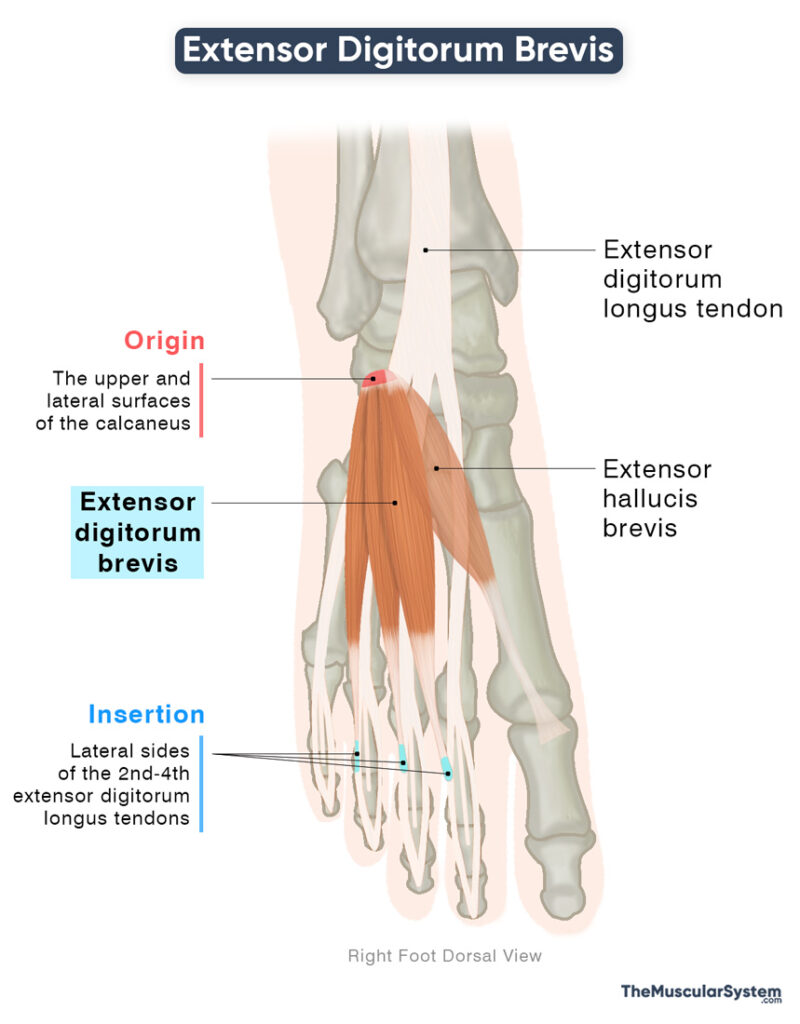
Location and Attachments
| Origin | The upper and lateral surfaces of the calcaneus bone |
| Insertion | The lateral sides of the 2nd-4th extensor digitorum longus tendons |
Origin
The muscle originates from the upper and lateral surface of the front part of the calcaneus (heel bone). It also arises partly from the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament, a fibrous band between the calcaneus and talus, and from the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum.
Insertion
The muscle fibers converge and form a short muscle belly, which then divides into four smaller slips. The most medial of these is known as the extensor hallucis longus, and is usually considered a separate muscle. The other three slips run forward over the dorsum of the foot to reach the second to fourth toes, where they insert into the lateral sides of the tendons of the second to fourth extensor digitorum longus.
The muscle may occasionally give off a tiny slip to the fifth toe or to the talus or navicular bones. Its belly may also partly blend with the dorsal interossei muscles, which lie between the metatarsal bones.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
On the dorsum of the foot, the EDB lies beneath the deep dorsal fascia, which is continuous with the inferior extensor retinaculum.
The muscle passes anteriorly over the calcaneus, cuboid, and lateral cuneiform bones, also lying superficial to the bases of the second to fourth metatarsals and the lateral terminal branch of the deep fibular nerve. Dorsally, the muscle is partly covered by the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus and the fibularis tertius.
Function
| Action | Extension of the 2nd to 4th toes at their interphalangeal joints |
The EDB muscle has no bony attachments within the foot, so it cannot act independently. Instead, it works together with the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) through its tendinous insertions to help extend the second to fourth toes at their distal interphalangeal joints. Since the EDB does not send a tendon to the fifth toe, extension of the little toe is handled entirely by the EDL.
Antagonists
The flexor digitorum longus and flexor digitorum brevis function antagonistically to the extensor digitorum brevis by flexing the lateral toes, opposing its action in extension.
Innervation
| Nerve | Deep fibular nerve (L5-S1) |
Innervation to the EDB muscle comes from the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve, derived from the fifth lumbar and first sacral nerve roots (L5-S1).
Blood Supply
| Artery | Dorsalis pedis and fibular arteries |
It is mainly supplied by branches of the fibular (peroneal) artery and the anterior tibial artery, which continues onto the top of the foot as the dorsalis pedis or dorsal artery of the foot. From the dorsalis pedis, smaller branches, including the lateral tarsal artery, arcuate artery, dorsal metatarsal, and digital arteries, provide additional blood supply.
References
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis: Meddean.LUC.edu
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle: Radiopaedia.org
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis: Elsevier.com
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts