Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis of the Foot
Last updated:
24/10/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis of the Foot
The flexor digiti minimi brevis (FDMB) is a small, thin muscle located on the lateral side of the foot, on the plantar side of the little toe. It is one of the three muscles in the third layer of plantar muscles, along with the flexor hallucis brevis and adductor hallucis. As its name suggests, the FDMB functions to flex the fifth digit (little toe).
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
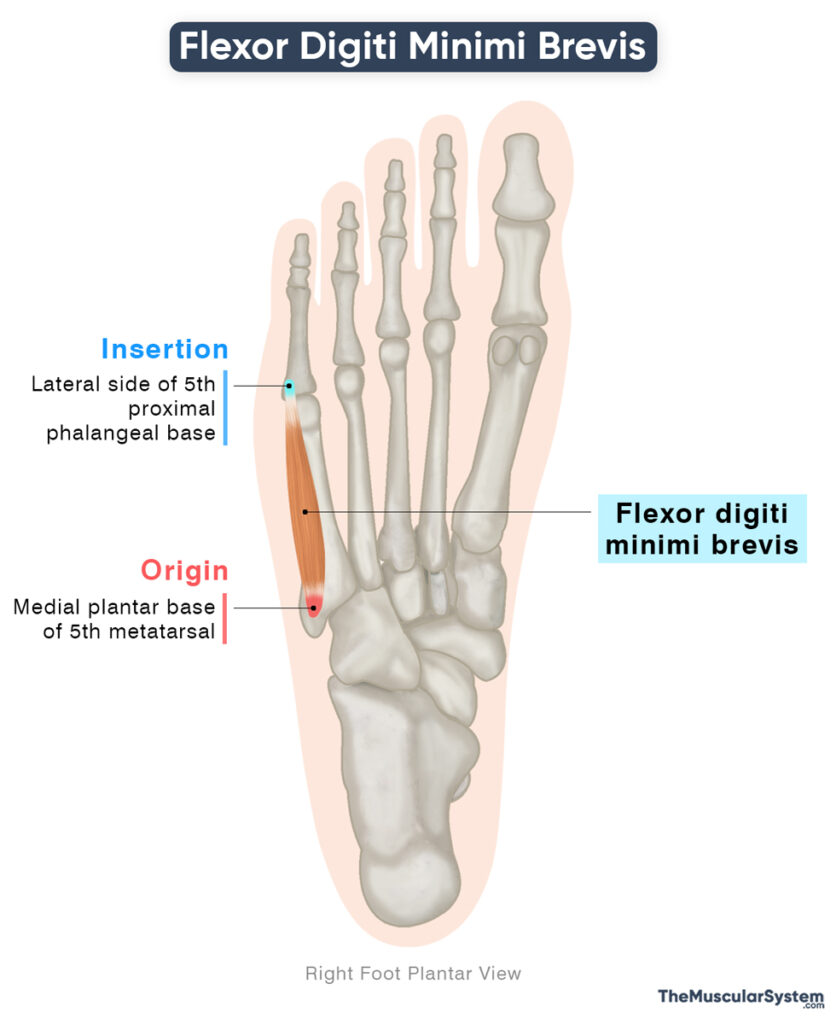
| Origin | Medial side of the plantar surface of the 5th metatarsal’s base |
| Insertion | Lateral side of the fifth proximal phalangeal base |
Origin
The muscle originates from the medial side of the plantar surface at the base of the fifth metatarsal, which is associated with the little toe. Additionally, part of its origin arises from the tendinous sheath of the fibularis longus muscle — a long muscle that extends from the proximal end of the fibula to the plantar surface of the foot.
Insertion
The muscle belly runs forward along the plantar surface of the fifth metatarsal, gradually narrowing into a small tendon. As it approaches the base of the little toe, the FDMB tendon merges with that of the abductor digiti minimi. The combined tendon then inserts into the lateral side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the fifth toe.
A deeper portion of the muscle may occasionally insert into the lateral aspect of the distal side of the fifth metatarsal. It is sometimes regarded as a distinct muscle, known as the opponens digiti minimi of the foot.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The FDMB is the most medially located muscle in the third plantar layer.
- Inferiorly, it is enclosed by the plantar aponeurosis.
- Superiorly, it lies beneath the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone and the interossei of the fourth plantar muscle layer.
- Medially, it is related to the third plantar interosseous and the fourth lumbrical muscles.
- Laterally, it lies next to the abductor digiti minimi muscle.
The lateral branch of the lateral plantar nerve passes superficially and medially to the muscle as it crosses the lateral surface of the sole.
Function
| Action | Flexion of the little toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint |
The FDMB acts to flex the little toe at the fifth metatarsophalangeal joint, bending it toward the sole. This movement contributes to both propulsion and stability during the gait cycle. Positioned on the lateral side of the sole, the muscle also supports the lateral longitudinal arch, helping to distribute the body weight efficiently during standing and walking.
It may also weakly assist the third interosseous muscle to adduct the little toe, meaning bringing it closer to the other toes.
The flexor digiti minimi brevis of the foot is analogous to the same-named muscle in the hand, which flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
Antagonists
The FDMB does not have any strong antagonists, but the abductor digiti minimi can be considered antagonistic to it, as it acts in the opposite direction by abducting the little toe. However, both muscles act in synergy to flex the little toe.
Innervation
| Nerve | Superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve (S2-S3) |
It receives innervation from the lateral plantar nerve, a terminal branch of the tibial nerve, carrying fibers from the second and third sacral nerve roots.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Lateral plantar, arcuate, and lateral tarsal arteries |
Blood supply to the muscle comes from the lateral plantar artery, which is a branch of the posterior tibial artery. The arcuate artery and the lateral tarsal artery, branching from the anterior tibial artery, also provide blood supply.
References
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis (Foot): TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Flexor Bigiti Minimi Brevis of the Foot: Kenhub.com
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis Muscle (Foot, Anatomy): PrimaryCareNotebook.com
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis (Foot): Radiopaedia.org
- Flexor Digiti Minimi of Foot: Elsevier.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Thyrohyoid
- -
Suprahyoid Muscles
- -
Geniohyoid
- All Posts