Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Last updated:
05/05/2023Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
The extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) is a long slender fusiform muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is one of the forearm’s 6 superficial extensors and one of the 3 muscles in the radial group of wrist extensors (mobile wad of Henry). The other two radial wrist extensors are the brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
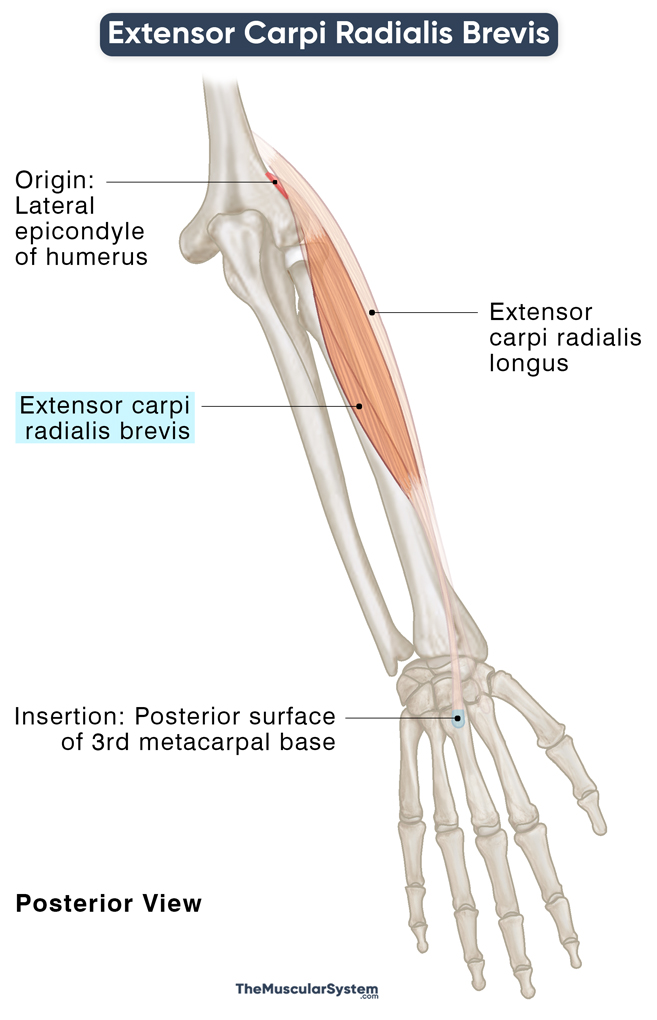
| Origin | Lateral epicondyle of the humerus (common extensor tendon) |
| Insertion | The posterior surface of the 3rd metacarpal base |
Origin
The muscle arises from the humerus’s lateral epicondyle via the common extensor tendon. The tendon gives rise to 3 other superficial forearm muscles, the extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris. A few muscle fibers arise from the lateral intermuscular septum, the barrier between the posterior and anterior compartments.
The radial collateral ligament, a short yet strong band of connective tissue that stabilizes the elbow, also serves as a secondary point of origin for ECRB.
Insertion
After originating, the muscle belly travels distally before narrowing down into a thin flat tendon halfway down the forearm. This tendon then travels further down, accompanied by the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon, to reach the wrist.
Around here, the ECRB tendon passes through the shallow groove at the posterior surface of the radius and underneath the extensor retinaculum to enter the hand dorsally. Finally, the tendon inserts at the base of the 3rd metacarpal (metacarpal of the middle finger) on the posterior surface.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The extensor carpi radialis brevis is the deepest muscle in the lateral compartment of the forearm. It lies deep to, and is partially covered by, the extensor carpi radialis longus. As their names suggest, the extensor carpi radialis brevis is smaller and thicker than the longus muscle.
On the distal side, the ECRB tendon runs deep to the deep posterior muscles extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus before passing underneath the extensor retinaculum. Here, the extensor carpi radialis longus tendon passes on the lateral side.
It can be palpated when the wrist is extended and abducted against resistance while keeping the hand pronated.
Since the extensor carpi radialis brevis works closely with the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle, it has the same antagonist in the superficial forearm muscle flexor carpi ulnaris.
Function
| Action | Extension and abduction of the hand at the wrist joint |
The muscle works with the extensor carpi radialis longus to extend the hand at the wrist joint while also playing an indirect but vital role in gripping something with your fingers.
For a firm grip, the hand needs to be extended at the wrist joint, with the flexor muscles blocked from acting to flex it. Because then the entire force resulting from the contraction of the flexor muscles will be transferred to the digits, producing a strong grip. An example of this movement is hitting a tennis backhand.
Another minor function of the muscle is to work with the flexor carpi radialis and extensor carpi radialis longus to abduct the hand on the radial or thumb side (radial deviation).
Innervation
| Nerve | The radial nerve’s deep branch (C7 and C8) |
The radial nerve, arising from the brachial plexus, directly innervates the muscle. Sometimes, the nerve supply may come from the posterior interosseous nerve, a branch of the radial nerve.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Radial artery |
The radial artery provides the primary vascularization, while additional blood supply comes from the radial recurrent artery (radial artery branch), and the radial collateral branch of the deep brachial artery.
References
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Forearm Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle: NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle: KenHub.com
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis: IMAIOS.com
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis: Rad.Washington.edu
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle: GetBodySmart.com
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis: Anatomy.app
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Laryngeal Muscles
- -
Thyroarytenoid
- -
Lateral Cricoarytenoid
- All Posts