Semispinalis Capitis
Last updated:
18/03/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Semispinalis Capitis
The semispinalis capitis is one of three semispinalis muscles, forming part of the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles. Along with the other semispinalis muscles (cervicis, thoracis), multifidus, and rotatores, it belongs to the deep back muscle group.
The muscle, located on either side of the vertebral column, extends from the upper thoracic spine to the base of the skull. It is the largest and most centrally located of the three semispinalis muscles, playing a key role in extending, tilting, and rotating the head and spine.
Anatomy
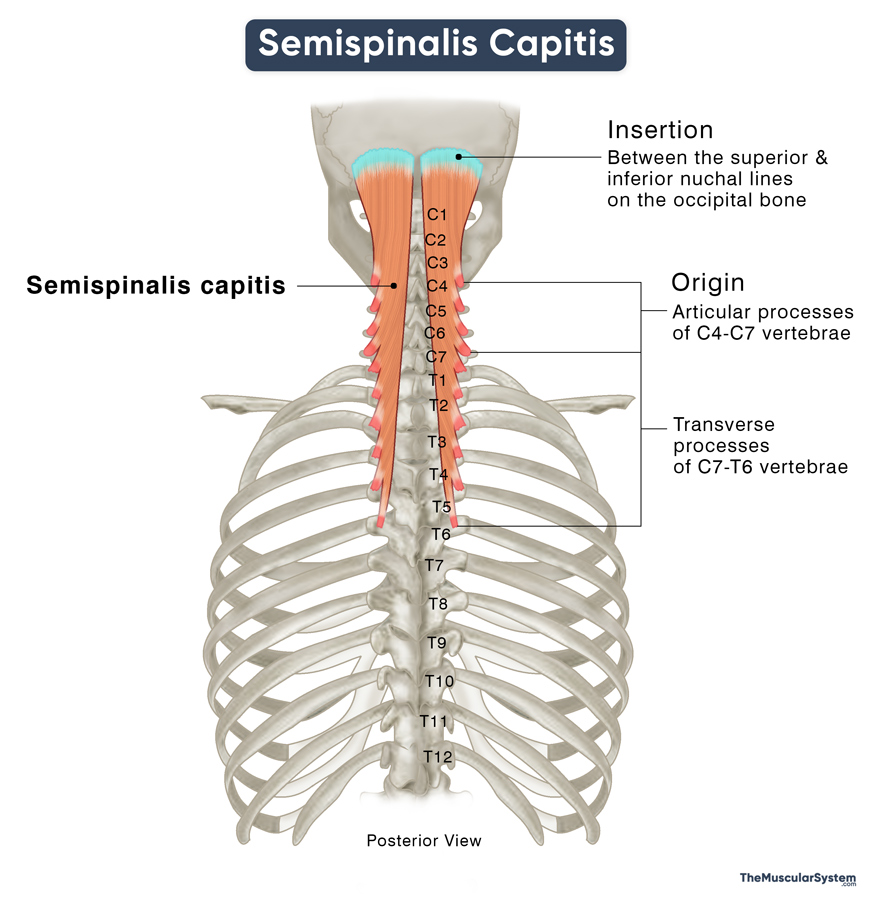
Location and Attachments
| Origin | Articular processes of C4 to C7 vertebrae, and transverse processes of C7 to T6 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Between the superior and inferior nuchal lines on the occipital bone |
Origin
The muscle originates from the superior and inferior articular processes of the 4th to 7th cervical vertebrae via narrow tendons, as well as from the tips of the transverse processes of the 1st cervical vertebra and the 1st to 6th thoracic vertebrae. The tendons converge to form a thick muscle belly, which courses upwards along the two sides of the vertebral column, between the shoulder blades.
Insertion
Once the muscle reaches the base of the skull, it inserts into the lower part of the occipital bone, between the inferior and superior nuchal lines.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The point of insertion of semispinalis capitis lies behind those of the neck muscles, obliquus capitis superior, and rectus capitis posterior major and minor.
It is the most superficial of the three semispinalis muscles, with the semispinalis cervicis lying medial to it. On the other side, its outer surface is covered by the splenius capitis. Semispinalis capitis also has the large triangular back muscle, the trapezius, lying superficially. The semispinalis muscles are also medial to the cervicis and capitis parts of the longissimus muscle.
The muscle is palpable as a firm, round structure in the back, beneath the trapezius, just lateral to the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Function
| Action | Extending, tilting, and rotating the head and neck |
When the muscle contracts on both sides (bilateral contraction), it assists the neck muscles, including the obliquus capitis superior and rectus capitis posterior major and minor, as well as the back muscles, splenius and trapezius, in extending the head, along with the cervical and thoracic spines. This action enables you to extend your head, neck, and upper back, such as when looking at something above your head.
When only one side of the semispinalis capitis contracts (unilateral contraction), it causes contralateral rotation of the head and neck, which means rotating the head toward the opposite side of the contracted muscle. Additionally, it contributes to ipsilateral lateral flexion, tilting the head toward the side of contraction. It is due to the muscle’s oblique orientation.
Innervation
| Nerve | Dorsal rami of C1 to C5 spinal nerves |
The muscle’s primary innervation comes from the posterior or dorsal rami of the 1st to 5th cervical nerves. The greater occipital nerve, which is the posterior ramus of the 2nd cervical nerve primarily responsible for innervating the muscles of the scalp, also contributes to the nerve supply to semispinalis capitis.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Occipital artery |
The blood supply primarily comes from the occipital artery, which arises from the external carotid artery — a major vessel running along the sides of the neck.
References
- Semispinalis Capitis | Origin, Insertion & Action: Study.com
- Semispinalis Capitis Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Semispinalis Capitis Muscle: Elsevier.com
- Semispinalis Capitis Muscle: GetBodySmart.com
- Semispinalis Capitis Muscle: IMAIOS.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts