Semispinalis Muscles
Last updated:
22/10/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What Are the Semispinalis
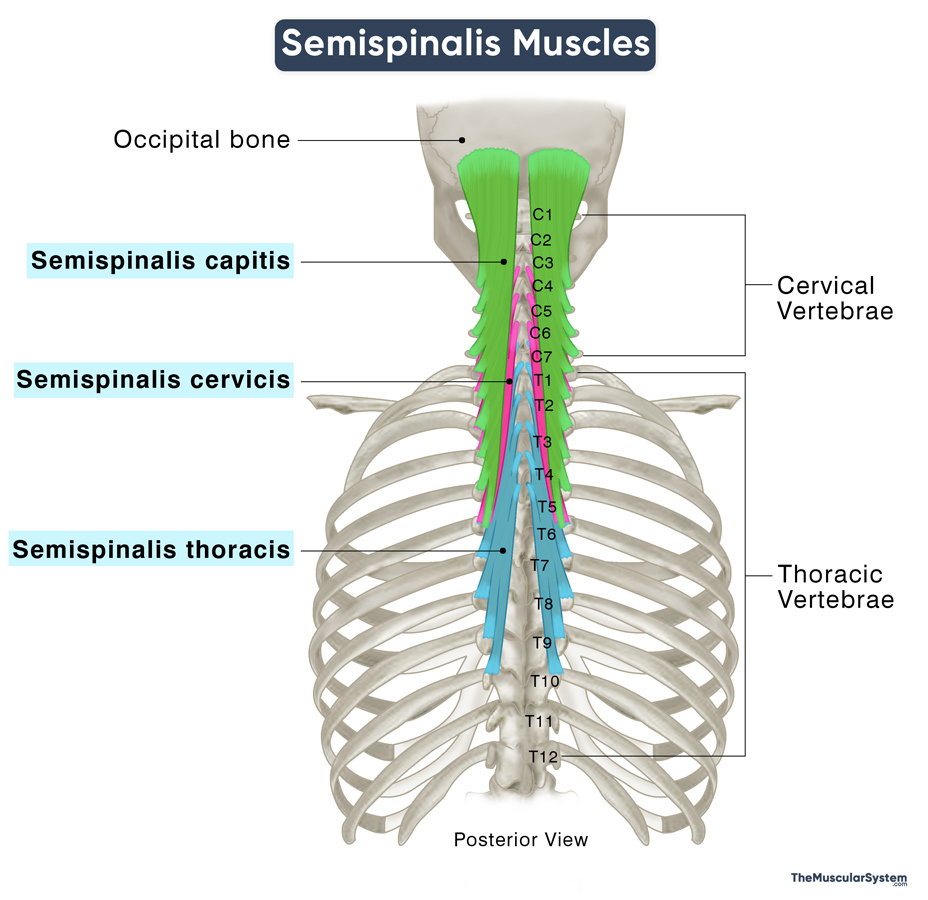
The semispinalis group comprises three long, narrow muscles: the capitis, cervicis, and thoracic. They form the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles along with the multifidus and rotatores. These 5 muscles together form the transversospinales group, one of the most important muscle groups in the human back.
The semispinalis, located along both sides of the thoracic and cervical spine, play a vital role in the movement of the head, neck, and back.
Names and Basic Anatomy of the Semispinalis Muscles
As is common with most other intrinsic back muscles, the 3 semispinalis are named after their points of insertion. Here’s a comparative overview of each:
| Name | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Blood Supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semispinalis Capitis | Articular processes of 4th-7th cervical vertebrae (C4-C7), and transverse processes of 7th cervical to 6th thoracic vertebrae (C7-T6) | On the occipital bone, between the superior and inferior nuchal lines | Extending, tilting, and rotating the head and neck | Dorsal rami of 1st to 5th cervical nerves (C1 to C5) | Occipital artery |
| Semispinalis Cervicis | Transverse processes of 1st-6th thoracic vertebrae (T1-T6) | Spinous processes of 2nd-5th cervical vertebrae (C2-C5) | Same as semispinalis capitis | Dorsal rami of the lower cervical nerves (C3 to C6) | Occipital, vertebral, and deep cervical arteries |
| Semispinalis Thoracis | Transverse processes of 6th-10th thoracic vertebrae (T6-T10 ) | Spinous processes of 6th cervical to 4th thoracic vertebrae (C6-T4) | Extending, tilting, and rotating the head, neck, and body trunk | Dorsal rami of cervical and thoracic nerves | Dorsal rami of the posterior intercostal arteries |
Semispinalis thoracis, with attachment to the lower thoracic vertebrae, is the only semispinalis muscle that participates in the movement of the entire body trunk.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle at the front of the neck, which helps flex the neck forward to bow your head, is antagonistic to the semispinalis muscles, as they extend the neck to bring the head back to an upright position.
References
- Semispinalis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Semispinalis Capitis Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Semispinalis Colli Muscle: Elsevier.com
- Semispinalis Thoracis Muscle: GetBodySmart.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts