Extensor Hallucis Brevis
Last updated:
08/10/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Extensor Hallucis Brevis
The extensor hallucis brevis, or EHB, is a small muscle located on the lateral side of the top of the foot. It belongs to the dorsal compartment of the foot, along with the extensor digitorum brevis. As its name implies, it works in synergy with the lower leg muscle, extensor hallucis longus, to extend the hallux or big toe.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
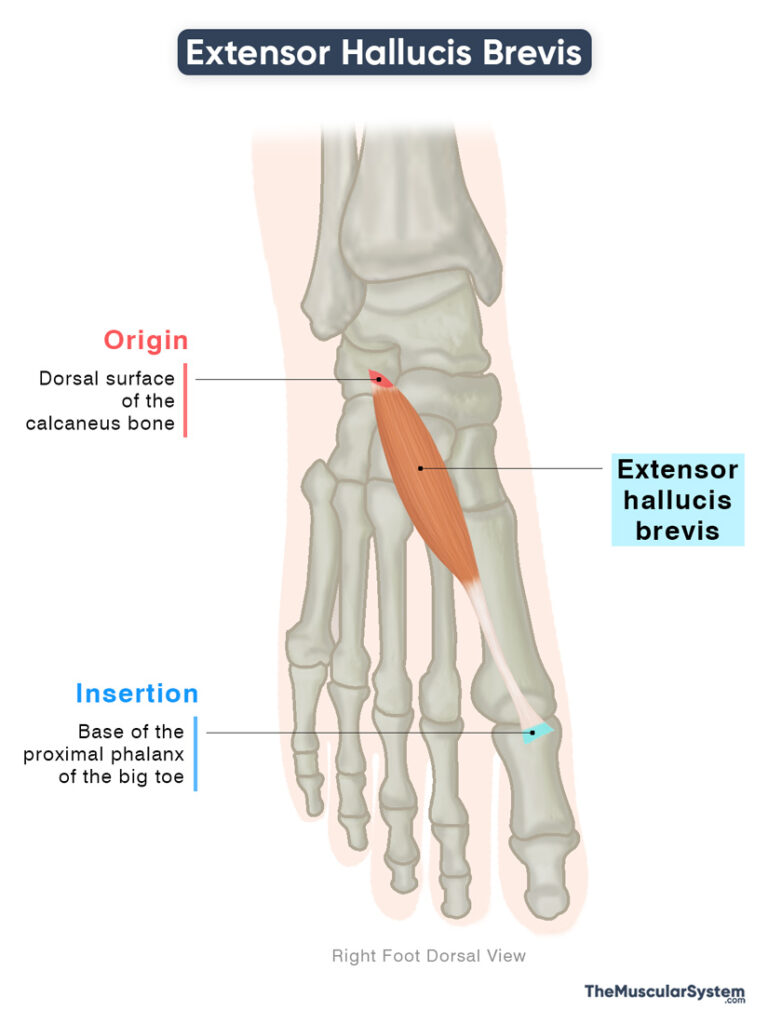
| Origin | Dorsal surface of the calcaneus bone |
| Insertion | Base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe |
Origin
The extensor hallucis brevis originates from the dorsal surface of the calcaneus, just proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint. It may also receive fibers from the inferior extensor retinaculum.
Insertion
From its origin, the muscle forms a short belly that courses anteromedially across the dorsum of the foot toward the great toe. It then tapers into a slender tendon that inserts onto the dorsal base of the proximal phalanx of the big toe.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The extensor hallucis brevis is the most medial muscle on the dorsum of the foot. In fact, it is sometimes considered to be the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis rather than a distinct muscle.
The EHB is superficial to the cuboid, the lateral and medial cuneiforms, the first metatarsal, also crossing over the dorsalis pedis artery and the deep fibular nerve. The muscle is covered by the deep fascia of the foot, which continues from the crural fascia of the leg.
It lies lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon, and medial to the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius
Function
| Action | Extension of the big toe at its metatarsophalangeal joint |
The muscle works with the extensor hallucis longus to extend the great toe (hallux) at the metatarsophalangeal joint. This movement helps lift the big toe off the ground during walking and running, preventing it from catching as the foot swings forward.
Antagonists
The flexor hallucis brevis functions antagonistically to the extensor hallucis brevis by producing flexion that opposes extension at the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation
| Nerve | Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve (L5-S1) |
The EHB receives innervation from the deep fibular nerve, which rises from the fifth lumbar and first sacral nerve roots (L5-S1).
Blood Supply
| Artery | Dorsalis pedis artery |
Blood supply to the muscle comes from the dorsalis pedis artery, also known as the dorsal artery of the foot. It is a branch of the anterior tibial artery, which supplies the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsal surface of the foot.
References
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis Muscle: Radiopaedia.org
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis: Elsevier.com
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis: Meddean.LUC.edu
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Temporoparietalis
- -
Corrugator Supercilii
- -
Depressor Supercilii
- All Posts