Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor
Last updated:
24/11/2025Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor
The rectus capitis posterior minor is a small, triangular, paired muscle located at the lower back of the neck, just at the base of the skull. It makes up the group of suboccipital muscles together with the rectus capitis posterior major, obliquus capitis superior, and obliquus capitis inferior.
The name of the muscle refers to its small size, with its Latin name musculus rectus capitis posterior minor meaning “the small straight posterior muscle of the head.” Though it works as a weak flexor of the head, stress or tightness of this muscle is often associated with headaches.
Anatomy
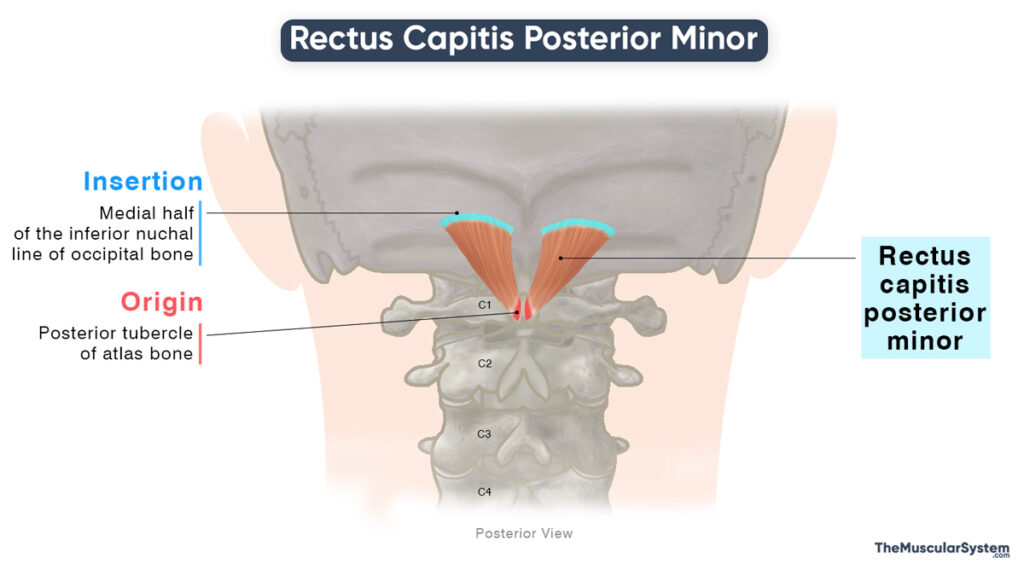
Location and Attachments
| Origin | Posterior tubercle of the atlas bone |
| Insertion | The medial half of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone |
Origin
The muscle originates via a thin tendon from the posterior tubercle of the atlas bone (C1 vertebra).
Insertion
From its point of origin, the muscle fibers course almost straight upward, slightly laterally. They fan out to form a thick, pyramid-shaped muscle belly which has a broad point of insertion along the medial half of the inferior nuchal line. This point of attachment usually extends to include the posterior surface of the occipital bone, just below the inferior nuchal line.
Part of the muscle also inserts into the posterior atlantooccipital membrane, a fibrous connective tissue between the occipital bone and atlas.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The rectus capitis posterior minor is the most medially located muscle within the suboccipital group, with the rectus capitis posterior major lying superficial and lateral to it. The left and right rectus capitis posterior minor muscles are positioned on either side of the midline at the back of the neck.
Directly superficial to the muscle is the semispinalis capitis, an intrinsic muscle of the back, while the posterior atlantooccipital membrane lies deep to it. Via the muscle’s insertion into this membrane, the rectus capitis posterior minor is indirectly connected to the spinal dura mater, the tough outer covering of the spinal cord.
Function
| Action | Extending the neck at the atlanto-occipital joint (weakly) |
It assists the other suboccipital muscles, mainly the rectus capitis posterior major and obliquus capitis superior, by acting as a weak extensor of the head. When the muscle contracts bilaterally, or on both sides, it helps extend the neck at the atlanto-occipital joint. Rather than producing large movements, this action helps maintain proper head posture.
The muscle is also believed to help stabilize the atlantooccipital membrane. And since this membrane connects it to the spinal dura mater, the rectus capitis posterior minor is thought to contribute to certain headaches that radiate from the back of the neck.
Antagonists
Since the muscle only acts as a weak extensor of the neck, it has no direct antagonists.
Innervation
| Nerve | Suboccipital nerve |
This muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve, which is the posterior primary ramus of the first cervical (C1) spinal nerve.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Vertebral artery and deep descending occipital artery |
Like the rest of the suboccipital muscles, blood supply to the muscle comes from the vertebral artery and the deep branch of the descending occipital artery, which itself is a branch of the external carotid artery.
References
- Rectus Posterior Minor Capitis Muscle: Elsevier.com
- Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Suboccipital Muscles: NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
- Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor: HealthLine.com
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts