Transversus Thoracis
Last updated:
11/06/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Transversus Thoracis
The transversus thoracis muscle, also known as the transverse thoracic muscle or triangularis sternae, is a thin band-like intrinsic muscle found on the inner surface of the front of the thoracic wall. It belongs to the group of intrinsic muscles of the thoracic wall with the intercostals, subcostals, serratus posterior, and levatores costarum.
Transversus thoracis are considered accessory respiratory muscles as they help with forced breathing.
Anatomy
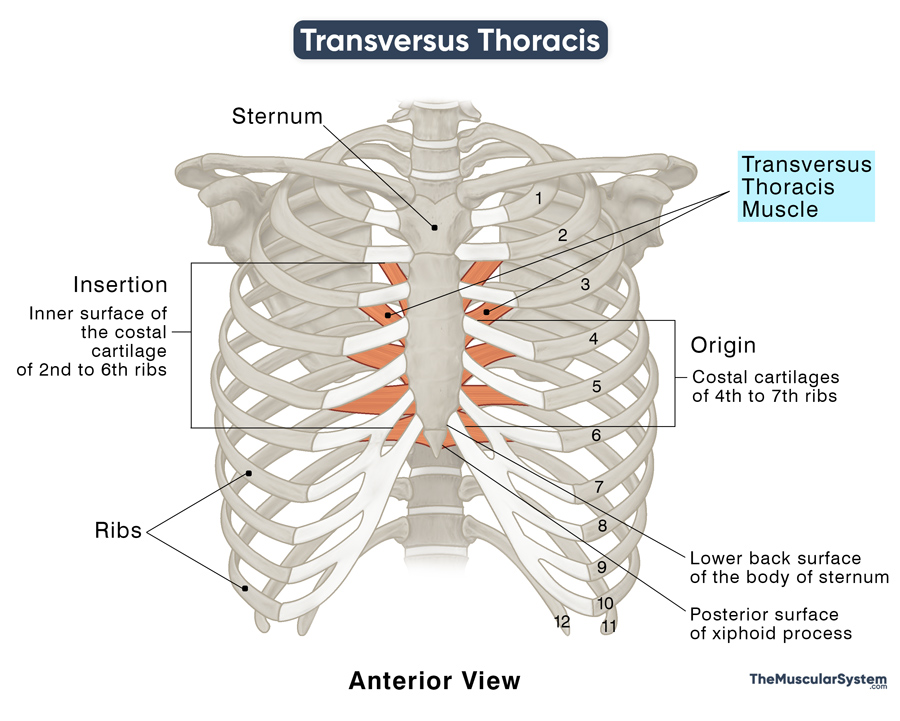
Location and Attachments
| Origin | Posterior surface of xiphoid process; the lower back surface of the body of sternum; costal cartilages of 4th to 7th ribs |
| Insertion | Inner surface of the costal cartilage of 2nd to 6th ribs |
Origin
The muscle originates and multiple thin muscular slips radiating from 3 points of origin:
- The inner or posterior surface of the xiphoid process
- The lower part of the posterior surface of the sternal body
- The costal cartilages and the sternal end of the 4th to 7th ribs — the lowest four true ribs
The flat ligamentous muscle slips course superolaterally, radiating toward the higher ribs.
Insertion
One by one, the slips are inserted into the inner aspect of the costal cartilages of the first six ribs, typically spanning from the 2nd to the 6th rib. The point of insertion can extend from the cartilage to the costochondral joints and the costal ends of the respective ribs.
The muscular slips that attach at the 6th ribs course almost horizontally. Those attaching into the higher ribs course at a 30-45° angle, becoming almost vertical at the highest insertion points.
Anatomical variations have been observed in these attachment points, even between the attachments on the left and right sides of the same individual.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The transversus thoracis muscle shares the same structural characteristics as the transversus abdominis muscle, while its lowermost muscular fibers also maintain continuity with it.
It lies deep to the thoracic cage on the anterior side of the body — the 2nd to 7th ribs, to be more exact. It is a vital position that allows the radiating strap-like slips of the muscle to contribute to the wall of the anterior mediastinum, particularly in the area directly behind the lower half of the sternum.
The transversus thoracis muscle also lies deep to the internal intercostal muscles, the upper six vessels of the anterior intercostal artery, and the intercostal nerves. The parietal pleura and endothoracic fascia lie superficially. So, the transversus thoracis muscle also acts as a barrier between the pleura and the intercostal nerves.
Function
| Action | Depressing the ribs |
As mentioned, the muscular bands course outward and upward as they attach to the ribs almost vertically. This gives them a considerable mechanical advantage over the ribs, especially the 2nd-6th, to depress them. It makes them useful during forced exhalation and for stabilizing the rib cage. In fact, with its unique shape and position, the transversus thoracis stabilizes the anterior side of the thoracic wall, keeping it from collapsing during inspiration.
Innervation
| Nerve | Intercostal nerves |
It is innervated by the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerve 2 to 6 (T2-T6), also known as the 2nd to 6th thoracic intercostal nerves.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Intercostal arteries |
The blood supply to this muscle comes from the anterior intercostal arteries that branch from the internal thoracic artery. The sternal branches of the internal thoracic artery serve as the primary source of vasculature.
References
- Transversus Thoracis Muscle: Elsevier.com
- Transversus Thoracis Muscle: Kenhub.com
- The Transversus Thoracis Muscle in Humans: CDM17018.Contentdm.OCLC.org
- Transversus Thoracis Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Transversus Thoracis Muscle: IMAIOS.com
- Muscles of the Thoracic Region: Med.UMICH.edu
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Thyroarytenoid
- -
Lateral Cricoarytenoid
- -
Transverse Arytenoid
- All Posts