Levatores Costarum
Last updated:
14/06/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What is the Levatores Costarum
The Levatores costarum, or levator costae, are 12 triangular paired muscles that attach the ribs to their adjacent thoracic vertebrae. Along with the intercostals, subcostals, transversus thoracis, and serratus posterior muscles, they belong to the intrinsic muscles of the chest that keep the rib cage stable during forced respiration.
Though it is categorized as a chest muscle here, the levatores costarum, along with the intertransversarii and interspinales, can also be considered one of the deepest back muscles.
Anatomy
Location and Attachments
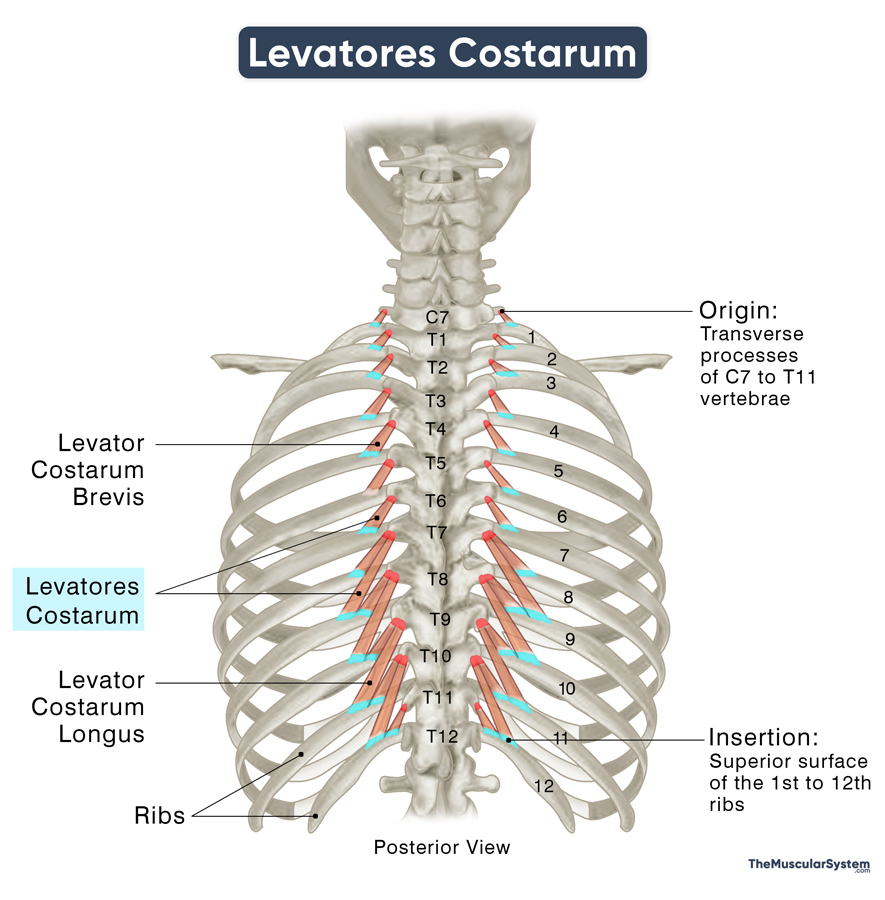
The small muscles are located along the vertebral column, one on either side of each vertebra from C7 to T11.
| Origin | Transverse processes of C7 to T11 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Superior surface of the rib immediately below the vertebra, each muscle originates from |
Origin
Each muscle pair arises from the tip of the transverse processes of the 7th cervical and 1st to 11th thoracic vertebrae. The muscle slips originate from a single point, fanning out as it courses toward their point of insertion, which gives them their triangular appearance.
Insertion
After originating, the muscles course downwards, laterally, and obliquely to insert into the ribs below their origin point. To be exact, they insert into the upper borders and outer surfaces between each rib’s tubercle and costal angle. For instance, the muscle pair originating from the sides of the C7 vertebra inserts into the 1st rib, while the next pair, originating from the T1 vertebra, inserts into the 2nd rib, and so forth.
The upper muscle bundles of levatores costarum remain single muscular strips throughout their course, from origin to insertion.
The lower muscles, typically after the T7 vertebra, divide into 2 muscle bundles or fasciculi:
- Levator Costarum Brevis: The shorter of the 2 fasciculi, it inserts into the rib immediately below the vertebra from which it originates.
- Levator Costarum Longus: It is the longer fasciculi that travels down to attach to the rib 2 levels lower than its point of origin. In simpler terms, if it starts from the T8 vertebra, it will connect to the 10th rib.
Relations With Surrounding Muscles and Structures
The levatores costarum is medial to the external intercostal muscles, with the fibers of both muscles coursing in a similar manner. It is lateral to the back muscles rotatores, intertransversarii, and muscles in the transversospinalis group. The semispinalis thoracis and cervicis from the transversospinalis group are superficial to the levatores costarum.
Function
| Action | Elevating the ribs to help with respiration |
Along with the other intrinsic muscles of the chest, it helps elevate the ribs and the thoracic cage to allow air to enter the lungs during inhalation.
Another action attributed to this muscle is assisting in the lateral rotation and flexion of the thoracic spine. However, more study is needed to understand its exact role and importance in these spinal movements.
Innervation
| Nerve | Posterior rami of C8-T11 spinal nerves |
Unlike the other chest muscles, the levatores costarum is innervated by the posterior rami of the spinal nerves C8-T11 — their lateral branches, to be exact. This innervation by the spinal nerves’ posterior rami contributes to some people’s classification of the muscle as a back muscle.
Blood Supply
| Artery | Posterior intercostal arteries |
The posterior intercostal artery’s dorsal branch supplies blood to this muscle. This artery is a direct branch of the thoracic aorta and travels along the inferior borders of the ribs.
References
- Levatores Costarum: TeachMeAnatomy.info
- Levator Costarum Muscle: RadioPaedia.org
- Levatores Costarum: IMAIOS.com
- Levator Costarum Muscle: Kenhub.com
- Levatores Breves Costarum: IMAIOS.com
- Levatores Costarum (Anatomy): GPNotebook.com
- Muscles Of The Thoracic Wall: Osmosis.org
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts