Splenius Muscles
Last updated:
07/10/2024Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
What are the Splenius Muscles
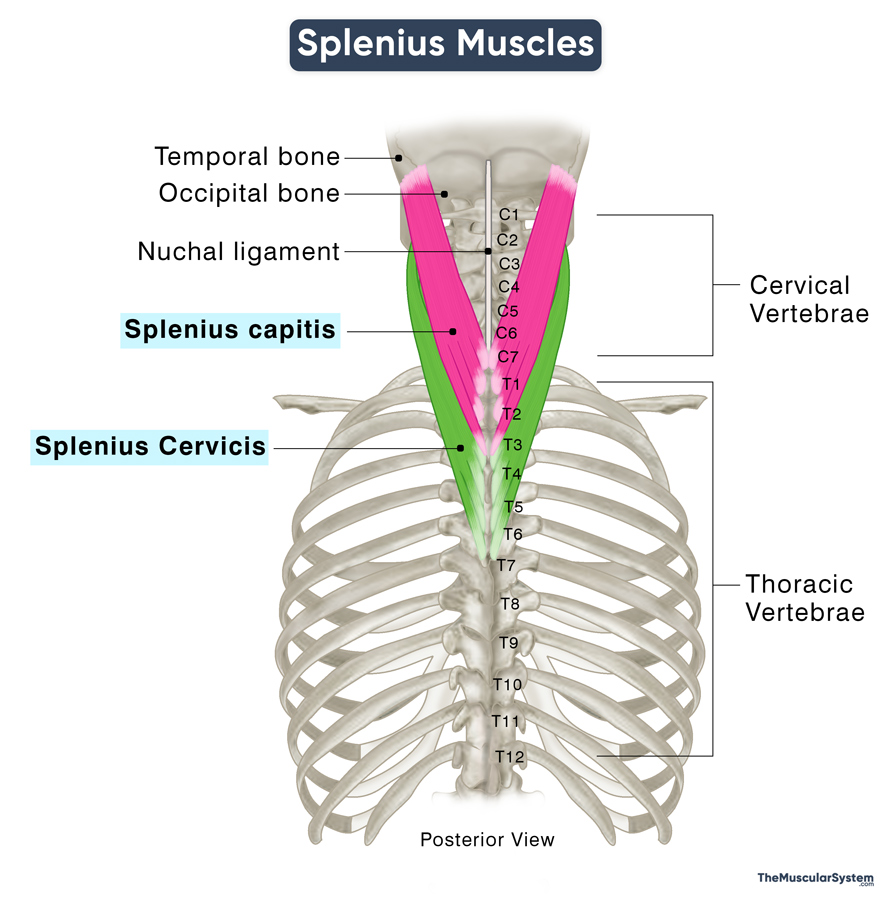
The splenius muscles are two paired muscles in the deep or intrinsic group of back muscles. They are the most superficial muscles in this group. Although both have their own distinct origin and insertion points, they work together seamlessly to facilitate extension, rotation, and stabilization of the head and neck.
Names and Basic Anatomy of the Splenius Muscles
| Name | Origin | Insertion | Actions | Innervation | Blood Supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
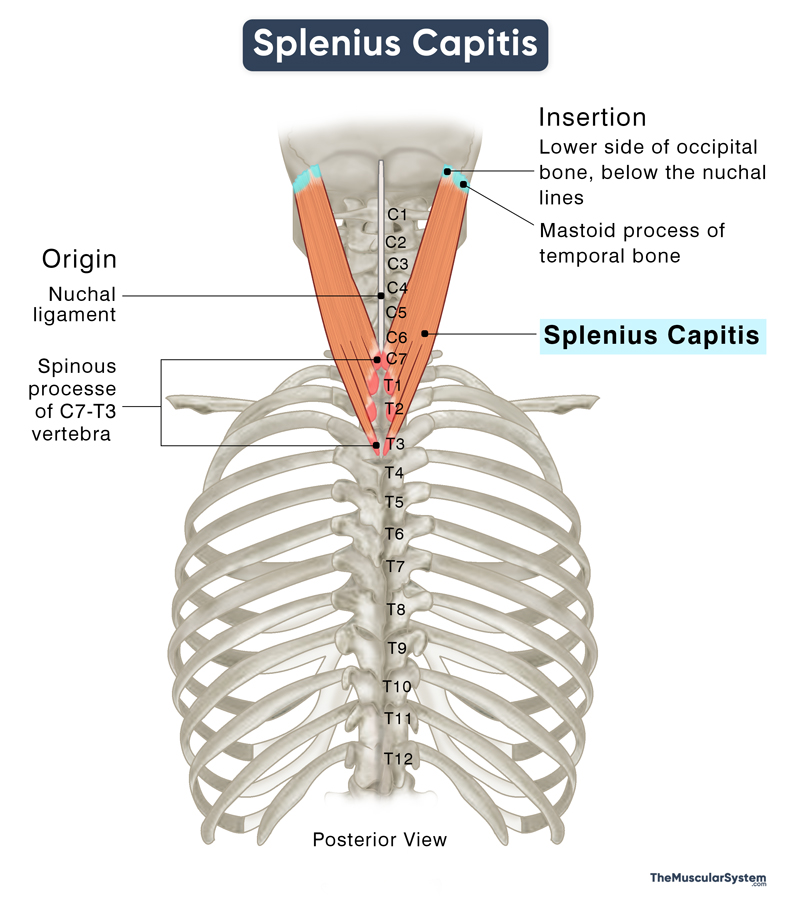
| Splenius Capitis | Spinous processes of the C7-T3 vertebra and the nuchal ligament | Spinous processes of the T3-T6 vertebrae | Extending, laterally flexing, and rotating the head and neck | Posterior rami of C2-C3 spinal nerves | Muscular branches of the occipital artery |
| Splenius Cervicis | The sides of the occipital bone and the mastoid process of temporal bone | Transverse processes of the C1-C3 vertebrae | The same as splenius capitis | Dorsal rami of the cervical nerves arising from the lower cervical vertebrae (C3-C7) | Transverse and deep cervical arteries |
The two muscles lie side by side in the neck, with the splenius cervicis running close along the lower lateral border of the splenius capitis. In this region, the two muscles may even blend, making it difficult to distinguish between the two.
Both muscles assist in extending the head and neck when they contract bilaterally. When they contract unilaterally, they help rotate and flex the head to the side.
Della Barnes, an MS Anatomy graduate, blends medical research with accessible writing, simplifying complex anatomy for a better understanding and appreciation of human anatomy.
- Latest Posts by Della Barnes, MS Anatomy
-
Tensor Tympani
- -
Stapedius
- -
Auricularis Posterior
- All Posts